Gum disease can be a lot more serious than you may think. The most common symptom of gum disease is bleeding gums, but other symptoms include pain while chewing or brushing your teeth, receding gums, and bad breath. Many people are unaware that they have it because the beginning of gum disease doesn’t always produce any warning signs. If you’re experiencing these symptoms, see your dentist immediately to prevent the progression of the infection and preserve your oral health.
What’s Gum Disease? (Beginning & Advanced)
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease (peri- means around; -odontal describes your teeth) begins with plaque buildup on your teeth and gums. Dental plaque, which is a sticky film of bacteria that forms on and in between the teeth. These bacteria feed on sugar and starches found in foods such as bread, pasta, candy, soda, etc., and produce toxins.
Gingivitis-causing bacteria in the plaque produce toxins that irritate and destroy the gums surrounding your teeth and advance below the gum line. Gum disease can be reversed at the beginning. However, if it is left untreated, it can lead to tooth loss. Stages of gum disease include:
- Gingivitis, an early stage that affects the gums surrounding your teeth.
- Periodontitis, an advanced stage that affects the soft tissues around teeth as well as the bone supporting them.
Prevention of gum disease is a vital component of dental care and overall health. Gum disease can be controlled by daily oral hygiene techniques, including brushing, flossing, regular checkups with your dentist, and regular professional cleanings. If you already have the early stage of gum disease, there are methods to reverse the damage.
Gum disease is a silent disease. You may not know you have it until the beginning of gum disease has progressed into periodontitis if you do not receive regular dental care.
Beginning Signs & Symptoms of gum disease
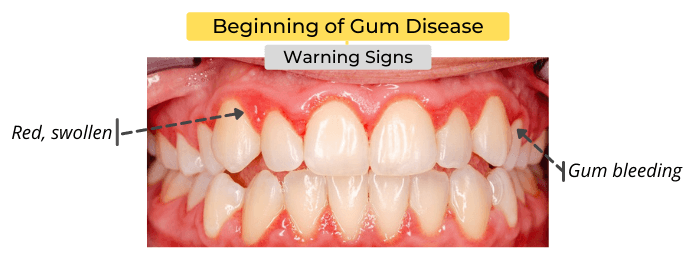
Gingivitis is the beginning stage of gum disease. The signs and symptoms of gingivitis include:
- Red or swollen gums.
- Bleeding while brushing your teeth, flossing, or after chewing food.
- Pain in your mouth that doesn’t go away.
- Presistant Bad breath despite good oral hygiene.
If you experience any of these early signs or symptoms, it is important to contact your dentist to reverse gum disease and keep your mouth healthy.
Signs & Symptoms of Periodontitis
Periodontitis is the advanced stage of gum disease. Its signs and symptoms include:
- Red or swollen gums, often with pus beginning to form underneath the gum line
- Blister-like sores on your gums and/or around your teeth.
- Your gum tissue starts to pull away from your teeth, exposing the teeth roots. This condition is known as gum recession.
- Tooth mobility and tooth loss.
If signs and symptoms of periodontitis occur, you must see a dentist as soon as possible. If left untreated for too long, this stage can lead to permanent tooth loss.
Causes & Risk Factors
Poor oral hygiene is the most common cause of gum infection. Harmful bacteria in the mouth can spread to your gums, damaging them and compromising their ability to heal. Also, bad breath occurs due to the buildup of sulfur-producing organisms such as Streptococcus mutans on teeth and gums. Other causes and risk factors of gum disease include:
- Diet and lifestyle: foods high in sugar increase your risk.
- Not flossing, not brushing your teeth properly.
- Smoking can lead to gum disease.
- Dry mouth condition.
- Age – as a person ages, the risk of gum disease increases.
- If you have diabetes, your gums can be damaged by high blood sugar levels.
- A diet low in vitamins A and C and poor nutrition overall also increases your risk for gum disease.
- Stress and anxiety Stress can affect your overall health, as well as the health of your teeth. It may disrupt the immune system (which fights infection) and cause ulcers to develop on the gums, which is a sign of early gum disease.
- Oral contraceptives (birth control pills) – combined estrogen/progesterone birth control pills increase the risk for periodontitis.
How Gum Disease is Treated?
If you are beginning to see signs and symptoms of gum disease, your best course of action is to get them treated as early as possible. The earlier a gum disease is caught, the less extensive treatment will be. It will also be easier for your dentist or periodontist to treat the problem and take preventative measures to prevent any further damage.
The first step in treating your gum disease is to understand what you are up against. Two main types of gum diseases can affect your mouth: gingivitis and periodontitis. Gingivitis affects the gums surrounding your teeth, while periodontitis affects the soft tissues around them as well as the bone supporting them. Both conditions eventually lead to tooth loss if they’re left untreated.
Treatment of The Beginning Stage of Gum Disease
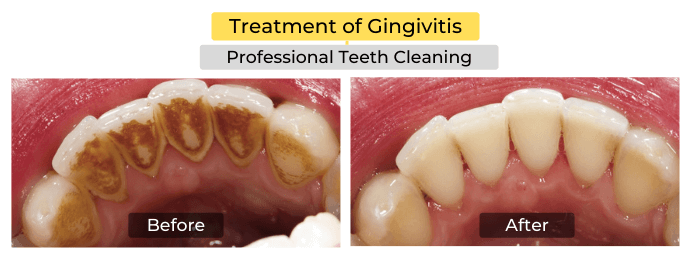
The treatment for the beginning stage of gum disease is non-surgical. Nonsurgical treatment may include scaling or root planing, which is the removal of the plaque and tartar from beneath your gum line. There are several ways you can treat the beginning of gum disease at home with simple lifestyle changes and over-the-counter treatments from your local pharmacy. Home remedies for gingivitis include:
- Brushing regularly with an antibacterial toothpaste twice each day.
- Flossing daily, using dental picks designed specifically for cleaning between teeth where plaque tends to collect.
- Use anti-bacterial mouthwashes.
- Limit sugary foods and drinks. Foods high in sugar encourage the growth of bacteria in your mouth.
- Using a tongue scraper to remove debris from the surface of your tongue.
- Visiting the dentist for professional teeth cleaning.
Treatment of Periodontitis
If the beginning of gum disease is left untreated, it can develop into periodontitis. At this more advanced stage, more drastic measures may be needed to prevent further damage. Your dentist will determine whether you are in early or advanced periodontitis and offer treatments accordingly. This treatment usually involves surgery to clean out pockets of bacteria beneath your gum line.
FAQ about The Beginning of Gum Disease
At the beginning stage of gum disease, there are no noticeable symptoms. However, gum disease can be spotted by a dentist or dental hygienist during an oral exam and cleaning. The dentist will look for red or swollen gums. Other signs to be on the lookout for include gum bleeding, persistent bad breath, and loose teeth.
There is no set time frame for gingivitis to develop into periodontitis, but studies have shown that gum disease can progress within as little as 3 months.
What puts you at an increased risk of gum disease includes poor oral hygiene, dry mouth condition, smoking, and diabetes. People with diabetes are three times as likely to develop gum disease. Smoking also causes a decrease in your body’s ability to fight infection and slows down the healing of wounds.
The best way to treat gum disease is to make an appointment with a periodontist. Your dentist will likely recommend some sort of non-surgical treatment such as scaling and root planing (deep cleaning), which will remove plaque and tartar from your teeth and gums, but if that alone does not get your gums healthy again, you may need surgery.