Like any area of your body, your mouth is susceptible to infection. Gum disease is a bacterial infection of the gums that damages the soft tissues and can destroy the tooth-supporting tissues. It usually arises from poor oral hygiene. However, several factors contribute to gum infection and gum diseases, such as smoking, hormonal changes, and diabetes mellitus. According to ADA, gum infection is a major cause of tooth loss in adults. In this blog post, we will discuss what causes infection of the gums, risk factors, symptoms, and treatment options.
What’s Gum Disease & Its Stages?
Gum disease is a bacterial infection of the gums. It can cause tooth loss if left untreated. Gum disease can be categorized into gingivitis and periodontitis.
- Gingivitis: It is the early stage of gum infection. It is characterized by inflamed, red gums and gum bleeding. Gingivitis can be reversed by professional teeth cleaning and oral hygiene habits. If gingivitis is left untreated, the infection may spread from the gums to the tooth-supporting tissues, causing periodontitis.
- Periodontitis: It is an infection of the gums and the tooth-supporting tissues. In this stage, the infection spreads to the tooth-supporting tissues, causing loose teeth and tooth loss.
Causes of Gums Infection
Gums infection usually occurs as a result of poor oral hygiene. Your mouth contains different types of bacteria. Good oral hygiene practices such as tooth brushing and flossing can help control the level of these bacteria and keep your mouth and gums healthy. Poor oral hygiene can promote the growth of bacteria, and allow the buildup of plaque around your teeth and gums.
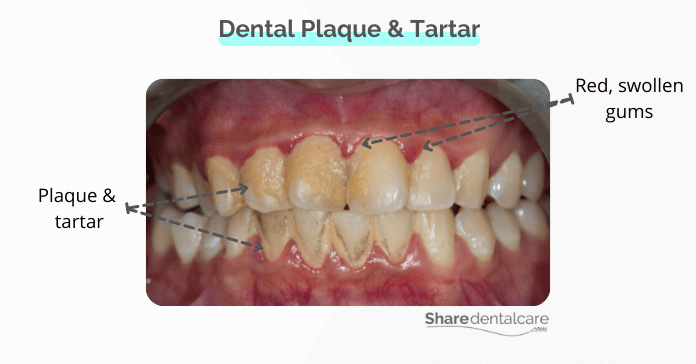
Dental plaque is a thin film of bacteria that accumulates on teeth every day. It can easily be removed with brushing and flossing. However, if plaque is not removed regularly, it will harden into tartar, which is only removed by professional teeth cleaning. Both plaque and tartar can irritate your gums and directly cause gum infection.
Risk Factors
The following factors increase your risk of developing gum disease:
- Poor oral hygiene such as not brushing or flossing your teeth.
- Smoking or chewing tobacco. You can read more about the link between smoking and gum disease.
- Hormonal changes during pregnancy (pregnancy gingivitis), puberty, and menopause.
- Dry mouth conditions.
- Broken tooth fillings and tooth decay.
- Poorly fitted dentures and dental bridges.
- Consuming certain medications such as calcium channel blockers, anticonvulsants, and steroids.
- Some diseases such as diabetes mellitus and HIV.
- Genetic factors.
How Do You Know That You Have Infection in the Gums?
Gum disease is a sign of overall poor oral health. The signs and symptoms of gum infection may vary, depending on the severity of the infection.
Symptoms of Gingivitis
In the early stage, most people aren’t aware that they have an infection in the gums or mouth because it causes no pain. The signs and symptoms of gingivitis include:
- Red, swollen gums.
- Gums are tender to the touch.
- Infected gums bleed easily when brushing or flossing your teeth.
- Bad breath.
Symptoms of Periodontitis
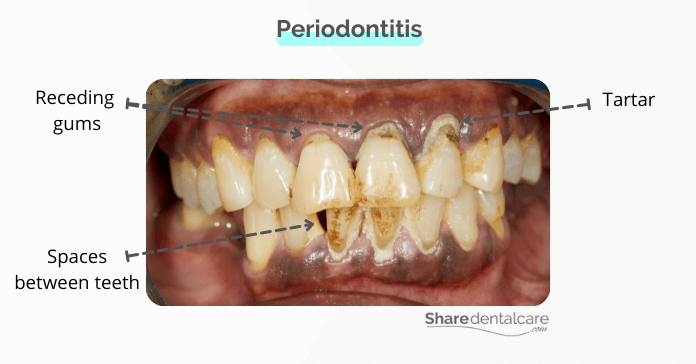
- Receding gums, gums begin to pull away from teeth.
- Teeth appear longer than normal because of the gum recession.
- Formation of periodontal pockets between teeth.
- Gum abscess, a pocket of pus in the gums.
- Changes in the way your teeth fit together when you bite.
- Sensitive teeth.
- Chronic bad breath, an unpleasant smell that doesn’t go away after you brush your teeth.
- Partial dentures are no longer fit.
- Loose teeth and eventually tooth loss.
How is Infection of The Gums Treated?
The treatment options vary, depending on the severity of the gum infection. Gingivitis can be reversed by proper oral hygiene and professional teeth cleaning at the dental office. However, if the infection of the gums is severe, further treatment will be needed. Treatment options include:
- Professional teeth cleaning (routine cleaning): In the early stage of gum disease, your dentist may use special instruments to remove plaque and tartar and prevent the spread of infection to the tooth-supporting tissues.
- Antibiotic therapy: Your dentist or periodontist may prescribe oral antibiotics and an antiseptic mouthwash to help control the infection in the mouth.
- Scaling and root planing (deep cleaning): If the infection extended to the tooth-supporting tissues, your periodontist may perform a deep cleaning to remove tartar from above and below the gum line and smooth rough root surfaces.
- Surgery: in severe cases, your periodontist may recommend surgery, for example,
- Gingivectomy: to remove the enlarged gum tissues.
- Flap surgery: to perform deep cleaning.
- Bone and tissue graft: to repair damaged gum tissues and bone.
Infection in The Gums – Conclusion
Gums infection usually occurs due to poor oral hygiene. Not brushing and flossing regularly can lead to the accumulation of dental plaque on your teeth. Plaque is a sticky film of bacteria that irritates your gums and can cause infection. If left untreated, the infection may spread to the tooth-supporting tissues, causing loose teeth and tooth loss.
The treatment options vary, depending on the severity of the infection of the gums. Gingivitis can be reversed by improving your oral hygiene and professional teeth cleaning. However, if the infection is more severe, you may need further treatment such as scaling and root planning. So, if you noticed any signs of gum infection, visit your dentist as soon as possible to receive treatment and prevent complications. Also, Maintain good oral hygiene to keep your mouth and body healthy.