Mouth cancer lesions, also known as oral cancer, are a disease in which some of the mouth’s cells grow out of control and may spread to other parts of the body. Mouth cancer can occur in the lips, gums, or tongue. If you are worried that you may have mouth cancer lesions, it is important to seek medical attention as soon as possible. In this blog post, we will discuss the symptoms of mouth cancer lesions, what to look for and how it is treated.
What Causes Mouth Cancer Lesions?
Mouth cancer lesions occur when cells in the mouth begin to grow and divide abnormally due to mutations in the cell’s DNA. These mutation changes can cause cells to behave and grow uncontrollably, eventually leading to cancer. Over time, mouth cancer lesions can spread inside the mouth and to other body parts, such as the head and neck.
Mouth cancer lesions are most commonly caused by changes (mutations) in the DNA of squamous cells. These are the thin, flat cells that line the lips and inside of the mouth. Most oral cancers are squamous cell carcinomas. The cause of oral cancer lesions is not fully understood, but it is thought to be linked with smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and other factors. Oral cancer can occur in:
- Lips
- Gums
- Tongue
- The floor of the mouth
- The roof of the mouth (hard palate)
- The inner lining of the cheeks
- Throat
Risk Factors
It’s not clear what causes these mutations in DNA. However, there are some factors that may increase the risk of mouth cancer lesions, such as:
- Smoking and tobacco use. Cigarette, cigar, or pipe smoking increases the risk of mouth cancer lesions and lung cancer. You can read more about how smoking can damage your teeth and gums.
- Alcohol consumption. Excessive alcohol consumption (more than four drinks per day) is a risk factor for mouth cancer lesions.
- Poor diet. A diet low in fruits and vegetables may increase the risk of cancerous lesions.
- Human papillomavirus (HPV). HPV is a virus that is transmitted through sexual contact. It is a risk factor for oral cancer and cervical cancer.
- Prolonged exposure to sunlight. Prolonged exposure to ultraviolet (UV) rays from the sun can increase the risk.
- Age. Oral cancer lesions are more common in people over the age of 40. However, it is crucial to be aware of the symptoms and risk factors regardless of age.
- Genetics. It can run in families. If you have a family member with cancer, you may be at increased risk.

Symptoms of Mouth Cancer Lesions
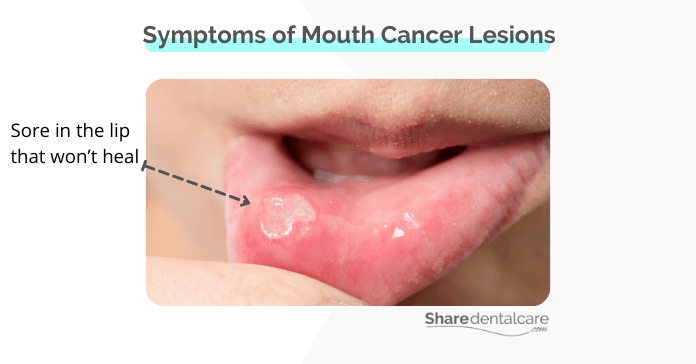
The most common symptom of mouth cancer lesions is a sore or lump in the mouth that does not go away. Other symptoms may include:
- Sore in the lip or mouth that won’t heal
- White or red patch on the gums, tongue, tonsil, or lining of the mouth
- Bleeding in the mouth
- Loose teeth and changes in the way teeth fit together
- Pain when swallowing
- Difficulty swallowing
- Numbness of the tongue or mouth
- Jaw pain and swelling
- Ear pain
- Weight loss
When to See a Doctor?
If you experience any of the symptoms listed above, it is important to see your doctor as soon as possible. They will be able to determine if you have oral cancer lesions or just an infection.
Oral cancer is easier to treat when it is caught early. If you wait too long, cancer can spread and become more difficult to treat. If you are worried about oral cancer lesions, the best thing to do is schedule an appointment with your doctor. They will be able to give you a thorough examination and determine if you need any further testing. You can read more about the early detection of oral cancer.
Types of Mouth Cancer Lesions
Oral cancer lesions are categorized by the type of cell they develop from. The most common type:
- Squamous cell carcinoma. It is the most common type of mouth cancer, accounting for about 90% of all cases. Squamous cell carcinoma starts in the thin, flat cells in the mouth.
Less common types:
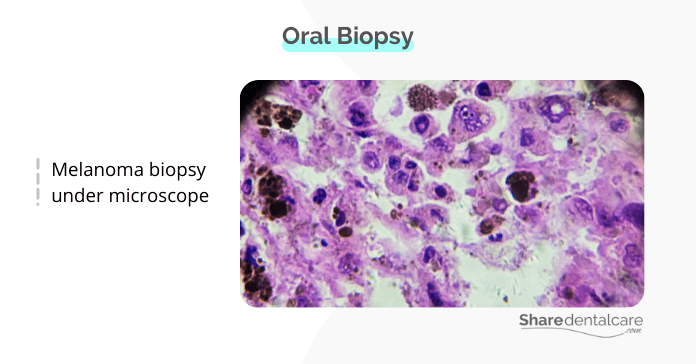
- Oral Malignant melanoma. This type starts in the melanocytes, the cells that give color to the mouth.
- Adenocarcinoma. This type starts in the salivary gland cells.
- Lymphoma. This type starts in the lymph node cells, part of the immune system.
- Sarcoma. This type starts in the bones, cartilage, muscles, and other tissue.
How Mouth Cancer Lesions are Diagnosed?
There are a few different ways that oral cancer lesions can be diagnosed. The first step is usually a visual examination of the mouth. Your doctor will look for any lesions or growths. If they see anything suspicious, they will order a biopsy.
- An oral biopsy is the removal of tissue to be examined under a microscope. The oral biopsy is the only way to definitively diagnose mouth cancer.
Other tests that may be ordered include:
- Blood tests. These are usually ordered to check for signs of infection or other conditions.
- X-ray. A dental or mouth x-ray can show if there are any abnormalities in the mouth.
- CT scan. It is a type of x-ray that creates a three-dimensional image of the mouth.
- MRI. This test uses magnetic waves to create a detailed image of the mouth.
- PET scan. This test looks for cancer cells throughout the body.
Mouth lesions can be benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous). Benign tumors are not as serious because they do not spread to other body parts. However, they can still be painful and cause problems if left untreated.
Malignant tumors are more serious because they can spread to other parts of the body. This is why it is important to see your doctor if you experience any of the symptoms listed above.
Treatment for Mouth Cancer Lesions
The treatment depends on the location and the stage of cancer. The treatment options include:
- Surgery. The goal of surgery is to remove the cancerous tumor and a margin of healthy tissue around it.
- Radiation therapy. This treatment high-energy beams, such as X-rays and protons to kill cancer cells.
- Chemotherapy. This treatment uses drugs to kill cancer cells.
- Targeted therapy. This treatment uses drugs that target specific genes or proteins that are found in cancer cells.
Prevention
The best way to prevent mouth cancer lesions is to:
- Quit smoking. Smoking is the leading cause of mouth cancer. If you smoke, quit as soon as possible.
- Quit drinking alcohol. Alcohol use is a major risk factor for mouth cancer.
- Eat a healthy diet. Eating a diet high in fruits and vegetables can help reduce your risk of mouth cancer.
- See your dentist regularly. Seeing your dentist for regular checkups can help catch mouth cancer in its early stages.
Mouth Cancer Lesions – Conclusion
Mouth cancer lesions occur when cells in the mouth grow out of control.
Tobacco smoking and alcohol drinking are the major risk factors for mouth cancer. Symptoms include mouth sores that do not heal, pain in the mouth, and difficulty swallowing.
If you have any concerns about mouth cancer lesions, the best thing to do is schedule an appointment with your doctor. They will be able to give you a more detailed examination and determine if you need any further testing.