Smoking has been linked to various health problems, and receding gums is just one of them. If left untreated, it can lead to more serious forms of gum disease and tooth loss. In this blog post, we will explore the link between receding gums and smoking. We will also discuss the treatments available for receding gums, and how to prevent them from happening in the first place. If you are a smoker, it is important to be aware of the risks associated with this habit and take steps to protect your oral health.
What are Receding Gums and What Causes Them?
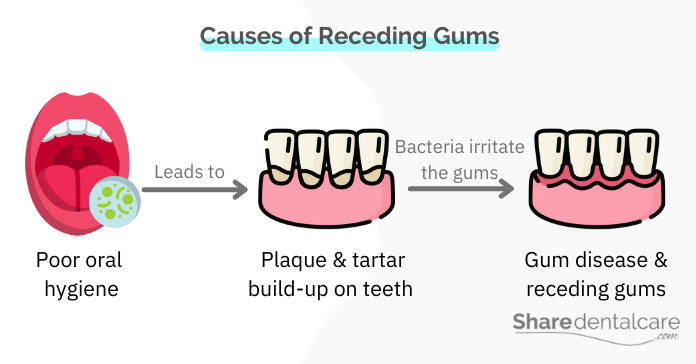
Receding gums is a condition in which your gums pull back from the tooth surface, exposing the root surfaces of your teeth. It’s a sign of gum (periodontal) disease, a bacterial infection of the gums and bone that support your teeth.
Gum disease starts with the buildup of plaque on teeth. Dental plaque is a sticky film of food debris, bacteria, and saliva. If plaque is not removed through daily brushing and flossing, it hardens into calculus (tartar). Once tartar forms, it can only be removed by a professional cleaning.
If plaque and tartar are not removed, they will begin to damage the gums and the bone that support teeth. This can cause the gums to recede or pull away from the teeth, exposing the roots and making teeth appear longer than they are. In advanced stages, receding gums can lead to tooth loss. You can read more about gum disease from tobacco smoking.
Risk Factors
There are several factors that increase the risk for receding gums, for example, smoking or chewing tobacco.
- Smoking and tobacco use. It includes cigarettes, cigars, pipes, and chewing tobacco. Smoking is one of the major risk factors for gum disease and receding gums.
- Poor oral hygiene. It means not brushing and flossing regularly or not doing so properly. Plaque and tartar build up on the teeth and gums, leading to inflammation.
- Hormonal changes. Pregnancy (pregnancy gingivitis), menopause, and other hormonal changes can cause gum tissue to become more sensitive and susceptible to inflammation.
- Certain medications. Some medications can cause dry mouth, which leads to an increased risk of gum disease.
- Medical conditions. Diabetes, HIV/AIDS, and other conditions can weaken the immune system and make it more difficult to fight infection.
- Genetics. Some people are simply more predisposed to receding gums and gum disease than others.
How Does Smoking Cause Receding Gums?
Smoking is one of the significant risk factors for receding gums. There are a few ways in which smoking contributes to this condition.
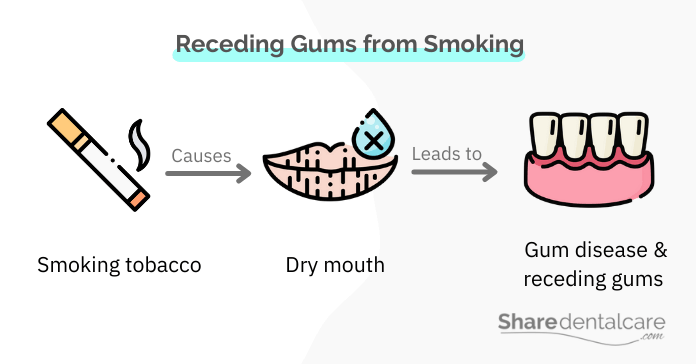
Smoking decreases the amount of saliva in your mouth. Saliva is important because it helps remove plaque and bacteria from your teeth and gums. Without enough saliva, plaque and bacteria can build up, leading to inflammation and receding gums.
Smoking damages the tissues in your mouth. The chemicals in cigarettes and other tobacco products can damage the gum tissue and make it more susceptible to infection.
Smoking decreases the blood flow to the gums. It can make it more difficult for the gums to get the nutrients and oxygen they need to stay healthy.
Smoking weakens the immune system. It makes it more difficult for your body to fight off infection, leading to receding gums.
Smoking prevents healing. If you already have receding gums or gum disease, smoking will make it more difficult for your gums to heal.
If you are a smoker, it is important to be aware of the risks associated with this habit and take steps to protect your oral health.
Complications of Receding Gums from Smoking
Gum disease can lead to many complications, including:
- Root decay. When the roots of your teeth are exposed, they are more susceptible to decay.
- Tooth loss. If receding gums are left untreated, the infection can spread to the tooth-supporting tissues, causing periodontitis, a more serious form of gum disease. It can cause bone loss and make your teeth fall out.
- Heart disease. Gum disease has been linked to heart disease, stroke, and other cardiovascular conditions.
- Diabetes complications. Gum disease can make it more difficult to control blood sugar levels in people with diabetes.
- Pregnancy complications. Gum disease has been linked to premature birth and low birth weight.
Smoking is a major risk factor for receding gums and other forms of gum disease. If you are a smoker, it is important to be aware of the risks and take steps to protect your oral health. If you have receding gums, it is important to see a dentist so that the condition can be treated.
How Do You Know if You Have Gum Disease?
To prevent gum recession, it’s important to know how to identify early signs and symptoms of gum disease. Look out for the following:
- Gums that bleed easily when brushing or flossing
- Red, swollen, or tender gums
- Gums that have pulled away from your teeth
- Persistent bad breath
If you notice any of these symptoms, it’s important to see a dentist or periodontist right away. They will be able to diagnose gum disease and recommend treatment.
Treatments for Receding gums from Smoking
There are a variety of treatments available for receding gums, depending on the severity of tissue loss. The earlier the diagnosis and treatment, the better the outcome. Smokers gums treatment options include:
- Quit smoking. It is one of the most important things you can do to improve your gum health. If you are a smoker, quitting smoking will help to reduce the risk of receding gums and other gum diseases. You can read more about do gums heal after quitting smoking.
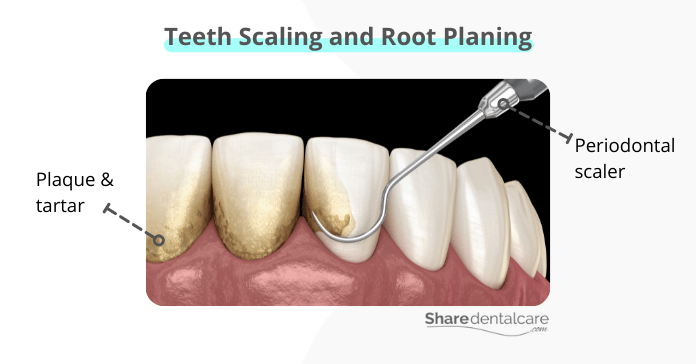
- Scaling and root planing. It is a deep cleaning procedure that removes tartar and bacteria from below the gum line. It can be done by a dentist or periodontist.
- Oral surgery: Your dentist may recommend oral surgery if your gum disease is advanced.
- Flap surgery. It is a more invasive procedure that involves lifting the gum tissue and removing tartar and bacteria from below the gum line. This can be done by a periodontist.
- Gum graft. It is a surgical procedure in which gum tissue is taken from another part of the mouth and grafted onto the receding gums.
- Bone graft. This is a surgical procedure in which bone is taken from another part of the body and grafted onto the jawbone to help support the teeth.
- Treatment of underlying conditions. If you have a medical condition contributing to receding gums, treating this condition can help improve your gum health.
Quit Smoking for The Prevention of Receding Gums
Smoking is a risk factor for gum disease, receding gums, and health problems, such as mouth cancer lesions. If you are a smoker, you should quit smoking or at least smoke in moderation to prevent oral health problems. Other ways to prevent gum recession include:
- Maintain good oral hygiene. Brush your teeth twice a day and floss daily.
- Use fluoride toothpaste. Fluoride can help to prevent gum disease and tooth decay.
- Eat a healthy diet. Eating a balanced diet is good for your overall health, including your gum and oral health.
- Limit sugary drinks. Sugary drinks can contribute to tooth decay.
- Visit your dentist regularly. Seeing your dentist for regular checkups and cleanings can help to prevent gum disease and other oral health problems.
If you are concerned about receding gums, talk to your dentist or periodontist. They will be able to diagnose the condition and recommend treatment. Early treatment is important for the best outcome. You can read more about bleeding gums after quitting smoking.
Receding Gums from Smoking – Conclusion
Receding gums is a sign of gum disease that causes the gum to pull away from the tooth surface. Smoking is a major risk factor for receding gums and other forms of gum disease because it dries out the gum and decreases blood flow to the gums. Smokers have twice the risk for gum disease in comparison with non-smokers.
Treatment depends on the severity of receding gums but typically involves quitting smoking, scaling and root planing, and treating underlying conditions. In advanced cases, your periodontist may recommend flap surgery, gum grafts, and/or bone grafts.