Do you have swollen gum pockets? If so, you may be suffering from periodontitis, an advanced stage of gum disease. Gum pockets are spaces that form between teeth and gums as a result of periodontitis. These pockets can become filled with food debris and bacteria, causing inflammation and swelling. If left untreated, gum pockets can lead to tooth loss. In this blog post, we will discuss the causes and symptoms of a swollen gum pocket, as well as the treatments available.
Why I Have Swollen Gum Pocket?
Healthy gums fit snugly around your teeth. But when you have periodontitis (an advanced stage of gum disease), the tissue and bone that support your teeth pull away. This can cause gum pockets to form between your gums and teeth. These gum pockets fill with bacteria and other debris, which can cause inflammation and swelling. As the disease progresses, these pockets deepen, and more gum tissue and bone are destroyed. Eventually, this can lead to tooth loss.
Not all gum pockets are swollen. Some may not cause any symptoms. But an infected and swollen gum pocket can be painful and make it difficult to eat or brush your teeth. A gum pocket can become enlarged and swollen as a result of:
- Inflammation and Infection. It occurs due to the buildup of plaque on teeth. Dental plaque is a sticky film that is made up of food debris, bacteria, and saliva. If plaque is not removed, it can harden and turn into tartar. The bacteria in plaque and tartar produce toxins that cause inflammation and swelling of the gums and pockets.
- Gingival abscess. It is a collection of pus that forms when a foreign body, such as food particles gets trapped between the gum and tooth.
- Periodontal abscess. It occurs when the gum infection spreads to the tooth-supporting tissues, causing the formation of an abscess.
- Periapical abscess. It occurs when the infection spreads to the tooth pulp. This may cause the formation of a pocket of pus at the root tip.
Risk Factors for Swollen Gum Pocket
The main cause of swollen gum pockets is periodontitis, an advanced stage of gum disease. This condition is caused by dental plaque, a sticky film of food debris and bacteria that forms on teeth. Plaque hardens into calculus, or tartar, which irritates the gums and causes inflammation. If plaque and tartar are not removed, they can damage the gum tissue and bone that support the teeth. This can lead to gum pockets. Several factors may increase your risk of periodontitis and swollen gum pockets, including:
- Poor oral hygiene. This is the most important factor that contributes to gum disease.
- Smoking and tobacco use. Smoking makes it difficult for your body to fight off infection. You can read more about receding gums from smoking.
- Age. Older adults are more likely to develop gum disease because of the decreased production of saliva, which helps to protect the teeth and gums.
- Diabetes. Diabetes mellitus can cause changes in the gum tissue that make it more susceptible to infection.
- Hormonal changes. Changes in hormone levels during puberty, pregnancy, and menopause can make the gums more sensitive and prone to inflammation.
- Stress. Stress can interfere with the body’s ability to fight off infection.
- Poor nutrition. Vitamin C and other nutrients are important for the health of gum tissue. A diet lacking in these nutrients can contribute to gum disease.
- Certain medications. Some medications, such as steroids and some cancer treatments, cause dry mouth, which increases the risk of gum disease.
- Genetics. Some people are more likely to develop gum disease because of their genes.
A Swollen gum pocket should not be ignored. If you suspect that you have a swollen or infected gum pocket, it is important to see a dentist as soon as possible. The sooner you begin treatment, the better your chances of reversing the damage and saving your teeth.

Symptoms Associated with Swollen Gum Pocket
A swollen gum pocket is a sign of periodontitis, a serious stage of gum disease. If you have swollen gum pockets, you may also experience the following symptoms:
- Gums that bleed easily when brushing or flossing.
- Swollen, red, or tender gums.
- Receding gums.
- Bad breath.
- Sensitive teeth.
- Pain when chewing.
- A pocket of pus in the gums.
- Loose teeth.
When to See a Dentist?
A swollen gum pocket should not be ignored. If you experience any of the symptoms associated with swollen gum pockets, it is important to see a dentist as soon as possible. The sooner you begin treatment, the better your chances of reversing the damage and saving your teeth.
Untreated gum disease can lead to tooth loss. Gum disease has also been linked to other health conditions, such as heart disease and stroke.
Treatment of Swollen Gum Pocket
The treatment of a swollen gum pocket will depend on the underlying cause and the severity of the condition. The treatment options include:
- Professional teeth cleaning. In mild cases of gum disease, a professional teeth cleaning may be all that is needed to remove the plaque and tartar from your teeth. This treatment can also help to relieve symptoms such as swollen gums and bad breath.
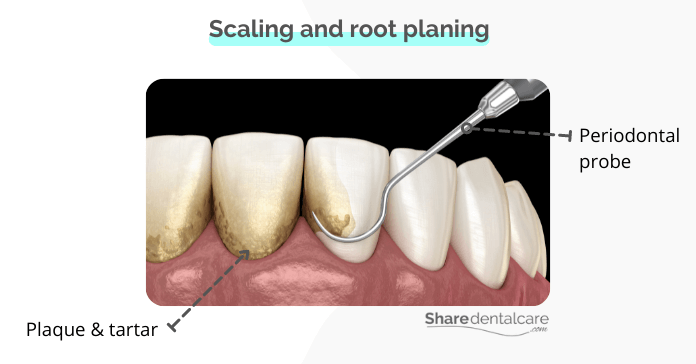
- Scaling and root planing. It is a deep teeth cleaning that is used to remove plaque and tartar from below the gum line. This treatment can also help to smooth out rough spots on the roots of your teeth, which can help to reduce inflammation and irritation. You can read more about the causes of loose teeth after deep cleaning.
- Antibiotics. If your gum disease is severe, your dentist may prescribe antibiotics to help kill the bacteria that are causing the infection. The antibiotics can be in the form of a pill, mouthwash, or gel.
- Surgery. In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to treat gum disease. The type of surgery will depend on the severity of the condition.
- Flap surgery (pocket reduction surgery). This procedure involves the lifting of the gum tissue and exposing teeth roots to perform a more effective scaling and root planning. The gum tissue is then stitched back into place.
- Gum grafts. If you have receding gums, your dentist may recommend a gum graft. This is a procedure in which healthy gum tissue is transplanted to the area where the gums have receded.
- Bone grafts. If you have lost bone due to gum disease, your dentist may recommend a bone graft. This is a procedure in which bone is transplanted to the area where the bone has been lost.
- Root canal treatment. If the infection spread to the tooth pulp, you may need a root canal.
- Tooth extraction. If the affected tooth is loose and can’t be saved, it may need to be extracted.
Home Care
At-home oral care is also important in the treatment of a swollen gum pocket. This includes brushing your teeth twice a day, flossing daily, and using an antibacterial mouthwash. Also, eating a healthy diet and quitting smoking can help to reduce pockets and treatment of gum disease.
It is also important to see your dentist regularly for checkups and professional teeth cleaning. This will help to remove plaque and tartar from your teeth and prevent the progression of gum disease.
Conclusion
A swollen gum pocket is a sign of periodontitis, a serious form of gum disease. In periodontitis, the gum tissue pulls away from the teeth and forms pockets. These pockets become filled with food debris and bacteria, causing the gums to become swollen and inflamed. If left untreated, gum disease can lead to tooth loss. You may also experience other symptoms such as bleeding gums, bad breath, and pain when chewing.
Treatment will depend on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. If you have a swollen gum pocket, it is important to see a dentist as soon as possible. The sooner you begin treatment, the better your chances of reversing the damage and saving your teeth.