Removable dentures are a common treatment for replacing missing teeth. However, they have some significant disadvantages. One of the biggest disadvantages of dentures is that they can slip out of place while you are smiling, eating, speaking, or coughing, causing embarrassing situations. This problem occurs due to the loss of the jawbone as a result of tooth loss. The loss of teeth leads to the loss of the height and thickness of the jawbone. Besides, wearing dentures accelerate the jawbone loss. Mini dental implants can prevent jawbone loss, and help stabilize your dentures.
The ideal treatment option for edentulous (toothless) patients with jawbone loss is bone grafting and conventional implants placement to support a bridge or denture. However, this treatment option is time-consuming and expensive. So, it is rejected by many patients. Mini dental implants may provide a solution for patients with jawbone loss or insufficient interdental space where conventional implants placement is not possible. In this article, we will discuss:
- Mini dental implants: uses, advantages, and disadvantages.
- Differences between conventional implants and mini implants.
- Mini implants procedure (step-by-step).
- Post-operative instructions following the mini implants surgery.
What are Dental Implants? (Conventional Implants)
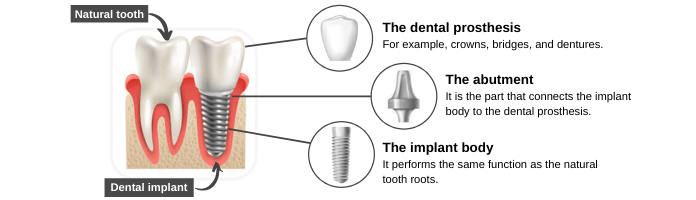
To fully understand mini dental implants, you should first know what dental implants are. Dental implants are artificial tooth roots that are placed surgically into the jawbone to provide support for crown, bridges, and dentures. The dental implants consist of three parts:
- The implant body: the dentist places the implant body in the jawbone. Then, the jawbone begins to fuse with the implant, making the implant permanently stable. This process is known as osseointegration, which can take from three to six months, depending on the quality of the bone.
- The abutment: This part connects the implant body to the dental prosthesis.
- The dental prostheses: there are two types of dental prostheses:
- Fixed such as crowns and bridges.
- Removable such as complete or partial dentures.
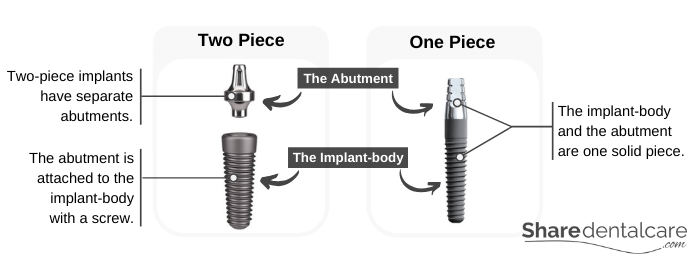
The implant body and the abutment can be connected (one-piece implant) or separated (two-piece implant). In the two-piece implant system, the dentist places the implant body in the jaw bone and leaves it for three to six months (the healing period). After the healing period, the dentist attaches the abutment to the implant body with a screw. While in the one-piece implant, the implant body and abutment are one solid piece. The two-piece implant system is more common because it is more flexible than the one-piece implant system. The diameter of conventional implants ranges from 3.4 to 6 mm.
What Are Mini Dental Implants?
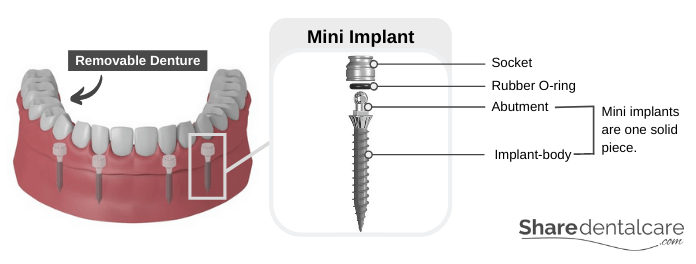
Mini dental implants are a one-piece implant system that has a small diameter. The diameter of mini implants ranges from 1.8 to 3.3 mm, which makes them suitable for narrow interdental spaces and patients with jawbone loss. Unlike conventional implants, mini dental implants have no separate abutment. The coronal portion of mini implants is the abutment, which appears as ball-head.
The dentist places the mini dental implants surgically into the jawbone, and the ball-head protrudes from the gingiva. Then, the dentist takes a dental impression and sends it to the dental laboratory for the fabrication of a denture. Typically, the denture contains sockets with rubber O-rings that attach to the ball-heads. According to the journal of oral implantology (JOI), you will need at least six mini implants in the upper jaw and four mini implants in the lower jaw to stabilize a complete removable denture. To support a fixed complete prosthesis, you will need at least ten mini implants in the upper jaw and eight mini implants in the lower jaw (in highly selected situations).
Uses of Mini Dental Implants
Mini dental implants are often used when conventional implants placement is not possible. The dentist uses the mini dental implants in only specific situations, which include:
- Replacing small teeth such as upper lateral incisors and lower incisors.
- Reduced interocclusal space: the space between the upper and lower jaw is small.
- Patients with jawbone loss, which prevents the use of conventional implants.
- Stabilization of partial or complete removable dentures.
- Support of fixed partial or complete prostheses (in highly selected situations).
Advantages
- Suitable for patients with low jawbone thickness.
- Minimally invasive surgical procedure. Because the dentist can place mini implants without complex flap surgery.
- No need for a bone graft because the diameter of the mini dental implants is less than 3 mm.
- Suitable for replacing small teeth such as upper lateral incisors and lower incisors.
- Immediate loading of the mini dental implants is possible (immediate function). You may receive a removable denture immediately after the procedure.
- Stabilization of complete or partial removable dentures. The stabilization of the removable dentures means more comfort and more natural use of the artificial teeth.
- Support partial or complete fixed prostheses (in highly selected situations).
- Less expensive than conventional implants.
Disadvantages
- Limited uses. The dentist often uses mini dental implants when conventional implants placement is not possible.
- The one-piece implants are less flexible.
- Support complete or partial fixed prosthesis only in highly selected situations.
- They Don’t anchor deep in the jawbone. So, loosening or the risk of loss is possible. The hold and stability of mini dental implants are limited.
- Implants with a small diameter have a greater risk of fracture.
- Not suitable for replacing central incisors.
Differences between Conventional Implants and Mini Dental Implants
| Types of Implants | Conventional Implants | Mini Implants |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | from 3.4 to 6 mm. | from 1.8 to 3.3 mm. |
| Design | Two-piece: have a separate abutment. This is the most common design. One-piece: the implant body and abutment are one solid piece. | One-piece: The coronal portion of mini implants is the abutment, which appears as ball-head. |
| Strength | Can withstand more pressure than natural teeth. | Implants with a small diameter have a greater risk of fracture. |
| Narrow spaces | Not suitable for replacing teeth with narrow interdental space. | Suitable for replacing small teeth such as upper lateral incisors. |
| Placement | They usually require two procedures. The first procedure is for the placement of the implant body. The second is minor for the attachment of the abutment. | They can often be placed in a single visit. |
| Bone grafting | You may need a bone graft in the case of the insufficient jawbone. Bone grafting can take up to 3 months or longer to heal before the placement of implants. | Usually, there is no need for a bone graft because they have a small diameter. |
| Healing time | Require a conventional healing period before the attachment of a prosthesis, which can take from three to six months. | You may receive a denture on the day of the surgery because the procedure is minimally invasive. |
| Loading of the implants | Delayed loading. Require a conventional healing period before the attachment of the final prosthesis. | Immediate loading. You may receive a denture on the day of the surgery. |
| Removable prostheses | Stabilize complete or partial removable dentures. | Stabilize complete or partial removable dentures. |
| Fixed prostheses | Support complete or partial fixed prostheses. | Support fixed prostheses only in highly selected situations. |
| Cost | Expensive. | Less expensive. |

Is Mini Dental Implants Suitable for You?
Removable dentures are a common treatment for replacing missing teeth. However, they have some significant drawbacks, for example, they can slip out of place while you are eating or speaking, causing embarrassing situations. Mini dental implants can stabilize removable dentures. Stable removable denture means more comfort and more natural use of the teeth. However, the denture remains removable. Generally, mini dental implants are not something you can choose but a treatment for patients who can’t be treated with conventional implants. You can benefit from mini dental implants for replacing missing teeth in places that have:
- Low bone thickness (bone graft is not possible).
- Narrow interdental space such as upper lateral incisors and lower incisors.
The mini dental implants procedure is a minimally invasive surgical procedure. So, it can be suitable for patients who can’t undergo major surgery due to health reasons. Since the hold and stability of mini dental implants are limited, patients should only use them if conventional implant placement is not possible.
Mini Dental Implants Could Be Suitable for You in These Situations:
- Stabilization of your removable denture.
- Replacing small teeth such as upper lateral incisors and lower incisors.
- If you can’t undergo major surgery due to health reasons.
- A bone graft is not possible.
- Conventional implants placement is not possible due to low jawbone thickness or narrow interdental space.
Contraindications
Mini dental implants are contraindicated in the following cases:
- Patients with frequent teeth grinding.
- Patients under 18 years old.
- During pregnancy.
- Heavy smokers.
- Patients who have medical conditions that may affect the healing process:
- Vascular conditions.
- Uncontrolled diabetes.
- Clotting disorders.
- Metabolic bone disorders.
- Patients who receive chemotherapy or radiotherapy.
Mini Dental Implant Procedure (Step-by-Step)
Pre-Operative Planning
First, your dentist will review your medical history. Because some medical conditions such as diabetes mellitus may affect the healing process, causing implant failure. Then, your dentist will examine your mouth with a mirror and probe and take a dental impression to make a study model. Also, your dentist will ask for a 3D x-ray (cone beam computed tomography) to check:
- The quality and quantity of jawbone.
- The location of anatomical structures such as nerves and maxillary sinuses.
Based on your 3D x-ray (CBCT) and study model, the dentist will make a treatment plan, which includes:
- Extraction of hopeless teeth remnants.
- Determining the number of mini implants needed to support a crown, bridge, or denture.
- Determining the suitable mini dental implants diameter, which ranges from 1.8 to 3.3 mm.
- Planning the exact position and angulation of the mini dental implants.
- Making a surgical guide for accurate, safe, predictable implant placement (in the case of guided surgery).
- Determining the type of final prosthesis (fixed or removable).
- Determining the type of anesthesia that will be used in the surgery.
Anesthesia
Since the mini dental implants procedure is oral surgery, you will need anesthesia to feel comfortable during the procedure. The anesthesia options include:
- Local anesthesia: usually, the dentist uses only local anesthesia for the placement of dental implants. It is the same type of anesthesia used in tooth filling, root canal treatment, or tooth extraction. The local anesthetic numbs the surgery area, and you will be awake during the procedure.
- Conscious sedation: Sometimes, the dentist may offer oral sedation or nitrous oxide in combination with local anesthesia to help you reduce anxiety and discomfort. Conscious sedation is beneficial for patients with extreme anxiety.
- General anesthesia: it is suitable for complex procedures. Under general anesthesia, you will be completely unconscious and will not feel anything around you.
The Placement Surgery
The placement of mini dental implants is similar to the placement of conventional implants. However, because the mini implants are smaller in diameter, the procedure is less invasive, takes less time, and has a shorter healing period than conventional implant procedure. Usually, the dentist or oral surgeon performs the mini dental implants procedure either with flap (conventional) or without flap (guided):
- Conventional surgery (with flap).
- Guided surgery (without flap).
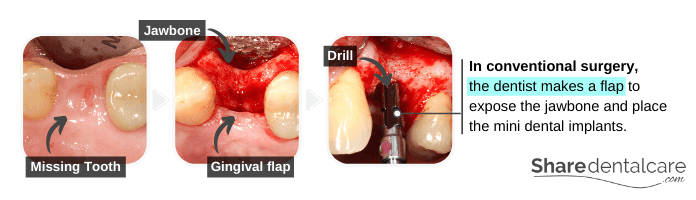
Conventional Surgery (with Flap)
First, the dentist makes a small incision (crestal incision) in the gum to expose the jawbone underneath. After making the flap, the dentist makes small holes in the jawbone and places the mini dental implants. Then, the dentist sutures back the flap around the mini implants. The ball-head protrudes from the gingiva.
Since the mini dental implants procedure is minimally invasive, the dentist may attach a complete removable denture to the implants immediately (immediate loading of the implants). In the case of fixed prostheses, you will receive the final crown or bridge after a conventional healing period (delayed loading of the implants). The healing period can take from three to six months, depending on the quality of the bone. You may receive a temporary prosthesis to wear during the healing period.
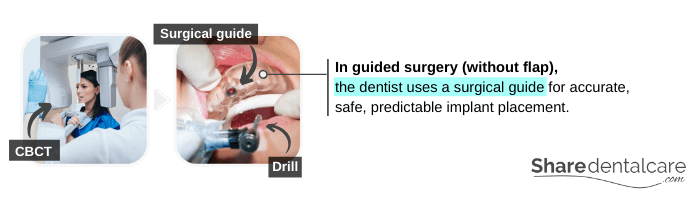
Guided Surgery (without Flap)
Based on your cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT), the dentist makes a surgical guide. This surgical guide ensures accurate, safe, predictable implant placement. Also, it minimizes the risk of pain and swelling. However, the surgical guide will increase the total cost of the procedure. After the placement of the mini implants, the dentist may attach a complete removable denture immediately (immediate loading). In the case of fixed prostheses, the dentist will recommend a conventional healing period (delayed loading), which can take from three to six months. You may receive a temporary prosthesis to wear during the healing period.
Healing Period
Osseointegration is the fusion between the implant and jawbone, which makes the implant stable. The osseointegration process takes from three to six months, depending on the quality of the bone. Usually, the dentist will attach a complete removable denture to the implants immediately. However, you may feel some discomfort during the first week.
In the case of fixed prostheses, the dentist will recommend a conventional healing period before attaching the crown or bridge (delayed loading). Because the fixed prosthesis may apply a great force on the mini implants, which can lead to the implant movement. The movement of the mini dental implants during the healing period can lead to implant failure. You may receive a temporary prosthesis to wear during the healing period.
The Dental Prostheses
Removable prostheses
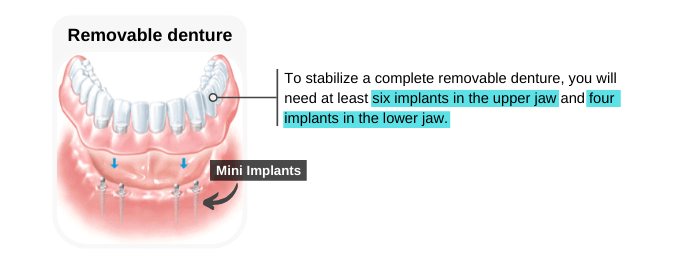
The dentist may use mini dental implants to stabilize complete or partial removable dentures, especially in patients with jawbone loss (atrophic ridge). To stabilize a complete removable denture, you will need at least 6 mini implants in the upper jaw and 4 mini implants in the lower jaw. After the placement of the mini implants, the dentist may attach the removable denture to the implants immediately (immediate loading).
Fixed Prostheses
Mini dental implants are suitable for the replacement of small teeth such as upper lateral incisors and lower incisors. Because small teeth have a narrow interdental space, and the placement of conventional implants with a regular diameter in these places is not possible. According to the Journal of Oral Implantology (JOI), the mini dental implants can be used to support a complete fixed prosthesis in highly selected situations.
To support a complete fixed prosthesis, you will need at least 10 mini implants in the upper jaw and 8 mini implants in the lower jaw. Generally, dentists use mini dental implants to support fixed prostheses when conventional implants placement is not possible. Dentists recommend a conventional healing period before the attachment of the fixed prostheses (delayed loading).
What to Expect After The Mini Implants Surgery?
The mini dental implants surgery is a minimally invasive procedure. However, you may experience:
- Discomfort.
- Minor bleeding.
- Swelling and/or bruising on your gums.
- Limited mouth opening.
- Swelling and/or bruising of your face.
These signs and symptoms are normal after the procedure. Your dentist will prescribe pain medications and anti-inflammatory medications to control these signs and symptoms. However, you should contact your dentist or surgeon immediately if the pain or swelling gets worse.
Instruction After The Mini Dental Implants Procedure
You should follow these instructions after the surgery to help speed the healing process.
In The First 24 Hours
- Take the prescribed medications.
- Maintain good oral hygiene. Brush your teeth with a soft-bristled toothbrush and avoid the surgical sites.
- Avoid things that may promote bleeding such as:
- Hot foods and drinks.
- Smoking.
- Spitting and mouth rinsing.
- Exercising or lifting heavy objects.
- Avoid aspirin.
- Apply cold compresses (ice-packs) to your face immediately after the procedure to minimize the risk of swelling.
- Avoid smoking and alcohol for a week following the surgery because they affect the healing process.
- Eat soft, cool foods such as ice cream, milkshake, pudding, eggs, and mashed potatoes.
- Avoid hard foods that may irritate the surgical sites such as popcorn, chips, and nuts.
- Avoid the use of straws because they may disturb the surgical sites.
- Ask a friend or family member to drive you home because you may not be able to drive.
After 24 Hours
- Maintain good oral hygiene and be careful around the surgical sites.
- Use a warm salt-water rinse for three days. (quarter teaspoon salt in a glass of water).
- Don’t smoke for a week following the surgery.
- Limit physical activities in the first 48 hours to prevent postoperative bleeding.
- Discomfort and swelling are normal after the procedure. So, continue taking the prescribed medications.
- Contact your dentist immediately if the pain or swelling gets worse.
Complications of the Mini Dental Implants Procedure
Like any surgical procedure, complications may occur:
- During the surgery.
- In the first six months.
- Long-term complications.
During the Surgery
There are always risks involved with any surgical procedure. The risks of the mini dental implants procedure include infection at the implant site, injury to nerves or blood vessels, perforation of the maxillary sinus, damage of the neighboring teeth, and lack of primary implant stability. So, the preoperative planning is important for the success of the procedure.
In the First Six Months
Sometimes, the mini dental implants may fail to fuse with the jawbone (failure of osseointegration), causing implant failure. The failure of osseointegration may occur due to several factors, such as:
- Poor oral hygiene.
- Smoking and alcoholism.
- Infection at the implant site.
- Lack of primary implant stability during the surgery.
- Uncontrolled diabetes and other conditions that may affect the healing process.
Long-Term Complications
Peri-implantitis: it is an inflammation around the implant, which leads to the loss of the bone supporting the implants. Peri-implantitis risk factors include:
- Poor oral hygiene.
- Smoking.
- Bruxism.
- Periodontitis.
- Uncontrolled diabetes mellitus.
FAQ
The major difference is that mini implants have a smaller diameter than conventional implants. The mini implants’ diameter ranges from 1.8 to 3.3 mm while the conventional implant’s diameter ranges from 3.4 to 6 mm. See the table above to know more about the differences.
Yes, mini implants can help prevent bone loss. Natural teeth preserve the jawbone’s height and width. Every time you bite or chew, the teeth roots stimulate the jawbone to grow and rebuild. When you lose your teeth, the jawbone begins to lose its height and width. Mini dental implants can preserve the jawbone’s height and width by providing the stimulation that missing teeth provided.
Several factors influence the cost of mini implants procedure such as your country, oral surgeon experience, type of surgery (conventional or guided), and the number of implants needed. The average cost of a mini dental implant ranges from 500$ to 1500$ per implant.
Mini dental implants are beneficial for patients who have missing tooth/teeth, and conventional implants placement is not possible. Candidates must have good general health, healthy bone, healthy gum, good oral hygiene, and can undergo oral surgery.
Summary
- Mini dental implants are a type of implant that has a small diameter. The diameter ranges from 1.8 to 3.3 mm, which makes them suitable for narrow interdental spaces and patients with jawbone loss.
- They are a one-piece implant system, which means that the implant body and abutment are one solid piece.
- The uses of mini implants include replacing small teeth and stabilization of partial or complete removable dentures.
- The dentist or oral surgeon performs the mini dental implants surgery either with flap (conventional) or without flap (guided).
- To stabilize a complete removable denture, you will need at least 6 mini implants in the upper jaw and 4 mini implants in the lower jaw.
- To support a complete fixed prosthesis, you will need at least 10 mini implants in the upper jaw and 8 mini implants in the lower jaw.
- Like any surgical procedure, there are potential risks. The risks of the surgery include infection, injury to nerves or blood vessels, perforation of the maxillary sinus, damage of the neighboring teeth, and lack of primary implant stability.