Smoking can cause many health problems, including lung cancer, cardiovascular disease, and stroke. While smokers might already know about these consequences of tobacco use, they may not realize that smoking also affects their oral health. Smoking contributes to gum disease, teeth discoloration, bad breath, and black gums. In this blog post, we’ll take a closer look at the causes and treatment of black gums from smoking.
What’re Black Gums from Smoking?
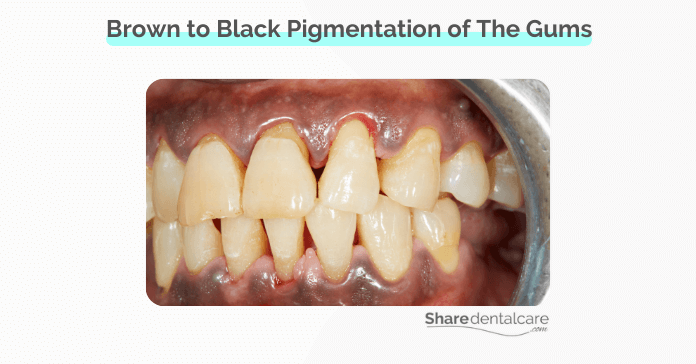
Smoker’s melanosis is an oral condition that causes brown to black pigmentation of the gums, cheeks, or palate. Dark gums from smoking are a result of chronic tobacco use. The pigmentation is not cancerous and will not cause any pain or discomfort. However, brown or black gums can ruin your smile, so you may need treatment to return gum color to normal. Learn more about tobacco’s effects on smokers’ teeth and gums.
Other Causes of Black Gums
In addition to smoking, there are other causes of black gums to consider before treatment. The causes include:
- Melanin is a substance that gives color to skin, hair, and eyes. If you have an excess of melanin in your tissue, it can give the appearance of black gums.
- Some medications such as acne medications.
- Some medical conditions may cause gums to develop darker pigmentation, such as:
- Acute Necrotizing Ulcerative Gingivitis (severe gum infection).
- Addison’s Disease.
- Oral Cancer.
- Peutz-Jeghers Syndrome.
Before the treatment of black gums, you should see a dentist and identify the underlying cause, for example, a genetic, smoking, side effect of some medications, or medical conditions.
How Smoking Contributes to Black Gums & Does It Require Treatment?
Healthy gums range in color from pink to brown or black, depending on an individual’s age and ethnicity. When you smoke, the nicotine and tar in cigarettes may turn the color of the gums to brown or black. This condition is known as smoker’s melanosis.
Smoker’s melanosis (black gums) occurs due to tobacco’s effect on melanocytes, the cells responsible for your skin, and gums’ pigmentation. When you smoke tobacco products, it releases chemicals that stimulate melanocytes into producing melanin, causing brown to black gums.
Black gums are a cosmetic condition that can lead to embarrassment when you smile. But it is not cancerous and doesn’t cause any pain or discomfort. Black gums from smoking don’t require treatment unless it affects your smile or self-esteem.
Treatment Options To Improve Black Gums from Smoking
You can turn your black gums to their normal color by quitting smoking. It usually takes from 3 months to 3 years for the black gums to return to normal. However, some people don’t want to go without cigarettes for that long or they can’t give up smoking.
In this case, you can turn your way back to a natural-looking smile by bleaching treatment in a dentist’s office. Gum bleaching, also known as gum depigmentation, can be used for the treatment of black gums from smoking tobacco products. Gum bleaching can make your smile look natural again.
The Gum Bleaching Treatment Process
Gum bleaching (depigmentation) is performed under a local anesthetic. The dentist removes the top layer of black gums, which contains the melanin pigment. During the healing, new gum tissues will grow and they will have a pink color rather than black. You should stop smoking after the procedure for at least 14 days to prevent complications. Also, try quitting smoking after the treatment to avoid the return of black gums.
The treatment has a short recovery time with some discomfort. It may take more than one session to get the desired gum color, depending on how dark and deep the pigmentations are. The dentist may use different methods to remove the black gums:
- Scalpel technique
- Cryosurgery (using extreme cold)
- Electrosurgery (using an electric current)
- Lasers (using laser beams)
Consult your dentist to know more about the treatment options for black gums from smoking. Learn more about the consequences of smoking after oral surgery.
Treatment of Black Gums from Smoking – Conclusion
Smoking is one of the leading causes of black gums. If you have black gums, then the best treatment is to quit smoking. your gums will return to their normal color within 3 months to 3 years. However, if that isn’t possible for you, your dentist may suggest gum bleaching treatment.
The process of gum bleaching involves removing the top layers of pigmented gums with different methods such as scalpel technique or laser. During the healing period, new gums with pink color will grow, making your smile look natural again. Consult your dentist to know in detail all the risks, benefits, and possible complications associated with the gum bleaching treatment.