Oral health is an important part of your overall health. Many smokers know the harmful effects of smoking on general health, but they don’t know the negative impact of smoking on oral health. Smoking and chewing tobacco increase the risk of gum disease, tooth decay, and oral cancer. Also, smoking tobacco for a long period of time may cause dark gums and teeth, which affect your smile and make you less attractive. In this blog post, we are going to talk about why dark gums from smoking happen and what you can do to get rid of this problem.
What’s Smokers’ Melanosis?
Tobacco smoke can irritate your oral tissues such as gums, cheeks, or palate, causing increased pigmentation or darkening of these tissues. This condition is known as smoker’s melanosis, which is a harmless, benign (non-cancerous) reaction from smoking and doesn’t lead to any other kinds of health problems. However, it makes your smile less attractive, which may cause decreased self-confidence.
Smoking tobacco causes dark (brown to black) pigmentation in the gums. These brown to black spots are melanin, which is a chemical substance produced by cells (melanocytes) that gives your skin, eye, and hair their color. The reason why gums turn dark after smoking for a long time is due to the increased melanin production.
Why Smoking Causes Dark Gums?
Healthy gums are usually pink in color. There are a few reasons why your gums become dark after smoking for a long time. Tobacco smoke contains nicotine and tar, as well as other chemicals, stimulate melanocytes to produce more melanin. The increased production of melanin leads to brown to black gums.
Also, smoking contributes to acute necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis (ANUG), also known as trench mouth, which is a bacterial infection of the gums. This kind of gingivitis not only causes darkening of your gums but also oral pain, bad breath, and bleeding from your gums.
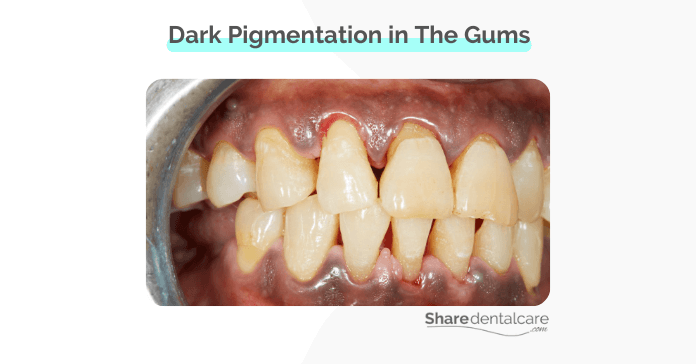
What Are the Effects of Dark Gums?
Smoker’s melanosis has no effects on your oral or general health. However, dark gums may make your smile less attractive, which causes decreased self-confidence and psychological impact. You may have less confidence to talk or smile in front of your friends and colleagues because of your dark gums.
How Long Does It Take for Gums to Become Dark from Smoking?
Apparently, there is no definite period of time to develop a smoker’s melanosis. It occurs gradually, and some people may have dark gums after smoking a few cigarettes a day, while others will not develop the condition unless they smoke about 20 cigarettes per day for many years.
Other Causes of Brown to Black Gums
In some cases, dark gums can be caused by other reasons than smoking. Causes of brown to black gums include:
- Genetics: some people are genetically predisposed to have dark gums.
- Some medications: dark gums may occur as a side effect of some medications such as antimalarials, antipsychotics, cancer therapy drugs, and some antibiotics. If you notice a change in the color of your gums after you start using a new medication, talk to your doctor.
- Certain medical conditions: dark gums may also be a sign of some medical conditions such as acute necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis (ANUG), Addison’s disease, Peutz-Jeghers Syndrome, and oral cancer.
Treatment Options of Dark Gums from Smoking
If you want lighter-colored gums, then quit smoking today. In most cases, your gums will return back to normal once you stop smoking. But if you can’t stop smoking immediately because nicotine is an addictive substance and you are still struggling with quitting, then your dentist may recommend gum bleaching treatment to lighten the affected areas.
In gum bleaching, your dentist uses a scalpel or other tools to remove the top layer of dark gums that contains excess melanin. After gum bleaching treatment, it takes 1-2 weeks for the affected gums to heal. During this period, a new gum tissue grows, and the gums will become lighter. The procedure is usually performed under local anesthesia and may cause some discomfort after the procedure. Gum bleaching can be performed with different tools such as:
- Scalpel
- Cryosurgery
- Electrosurgery
- Lasers
While gum bleaching is an effective treatment for smokers’ melanosis, it doesn’t solve the underlying reason for your dark gums, which is smoking. If you continue to smoke, your gums will become dark again. So the best way to avoid further darkening of your gums is to quit smoking completely. Learn more about the treatment of black gums from smoking.
How long Does It take for Dark Gums to Return to Normal after Quitting Smoking?
After you stop smoking, it usually takes from 3 months to 3 years for your gums to become back to normal. This varies, depending on how long you have been smoking and the number of cigarettes smoked per day. Some people will notice their gums returning to normal within several months, while others may need one to two years or more for this period.
Dark Gums from Smoking – Conclusion
Smoker’s melanosis is the darkening of gums, cheeks, or palate due to smoking. While dark gums from smoking have no effects on your oral or general health, this condition may make you less confident and self-conscious about smiling or talking in front of others. If this bothers you enough that you want to do something about it, talk with a dentist who can help lighten your gums by performing gum bleaching treatment. The best way to treat dark gums is to quit smoking, which will help you return your gums to their original color and make you healthier.