Gingivitis is a mild form of gum disease that causes inflammation, redness, and swelling of the gums. If left untreated, the infection may spread and damage the tooth-supporting tissues, causing periodontitis, a progressive form of gum disease. Untreated gum disease can lead to complications, such as pain, dental abscess, and tooth loss. In this blog post, We will discuss how gingivitis occurs and whether it is contagious.
How Does Gingivitis Occur?
Gingivitis usually occurs due to the build-up of plaque on teeth, a sticky, colorless film of bacteria. These bacteria produce toxins that irritate the gums, causing inflammation, redness, swelling, and gum bleeding. Ignoring these signs can lead to gingivitis progressing into periodontitis, which damages the bone and tissues supporting your teeth.
You can easily remove dental plaque by brushing and flossing your teeth regularly. However, if not removed regularly, plaque can harden into tartar, which is difficult to clean. In this case, you will need to visit your dentist for professional teeth cleaning. The good news; you can reverse gingivitis by improving your oral hygiene and professional teeth cleaning.
Is Gingivitis Contagious?
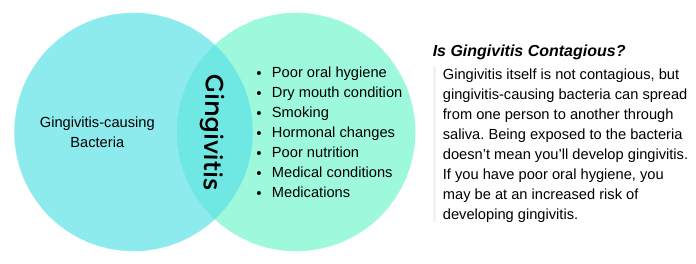
Gingivitis itself is not contagious, but the bacteria that cause it are. Gingivitis-causing bacteria include:
- Streptococcus mutans
- Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans
- Porphyromonas gingivalis.
These bacteria can spread from one person to another through saliva or shared foods and drinks. Exposure to these bacteria will not cause gingivitis, but other factors must be involved.
Risk Factors
The bacteria that cause gingivitis are contagious; they can be passed from one person to another by kissing or sharing drinks. If you kiss or share drinks with someone who has gingivitis or periodontitis, you will be exposed to these bacteria, but that doesn’t mean you will develop gingivitis. Bacteria alone will not cause gingivitis, but other factors must be involved.
The following factors may weaken your immune system, making it easier for bacteria to grow and harder for your body to fight gingivitis.
- Poor oral hygiene: It encourages the accumulation of plaque on teeth surfaces. Dental plaque produces toxins that cause inflammation of the surrounding gum tissues. Also, food particles provide an ideal breeding ground for bacteria to grow.
- Dry mouth condition: Saliva fights bacteria and neutralizes acids produced by them. A dry mouth can allow gingivitis-causing bacteria to grow.
- Smoking and chewing tobacco: Smoking weakens your immune system and makes it harder for your body to fight infections. Also, smoking can cause dry mouth conditions. Some research has shown that smoking increases the risk of gingivitis and periodontitis.
- Hormonal changes can cause gingivitis during pregnancy and the menstrual cycle.
- Poor nutrition: for example, vitamin-C deficiency. If your diet lacks some nutrients, it may be more difficult for tissues in your mouth to fight infection.
- Some medical conditions: such as diabetes mellitus, and certain viral and fungal infections
- Some medications: oral health may be affected by some medications, especially if they cause dry mouth as a side effect.
You can read more about the link between smoking and gum disease.
How Does Gingivitis Bacteria Spread?
Gingivitis itself is not contagious, but the bacteria that cause it can spread through saliva. This means that the risk of gingivitis increases with saliva-to-saliva contacts, such as kissing, or sharing cups, straws, toothbrushes, and eating utilities.
If you have kissed or shared a drink with someone who has gingivitis or periodontitis, this doesn’t mean you will develop gingivitis, but gingivitis-causing bacteria could be passed to you. Don’t worry if you have good oral hygiene. Also, saliva plays an essential role in oral health;
- Keeps your mouth moist.
- Fights bacteria in your mouth.
- Neutralizes acids produced by bacteria, preventing dental caries and gingivitis.
- It contains minerals that help reverse the early stage of tooth decay (remineralization).
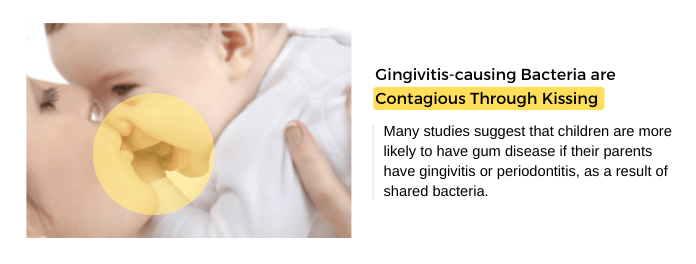
Gingivitis Bacteria are Contagious Through Kissing
Gingivitis and periodontitis themselves are not contagious but bacteria such as A. actinomycetemcomitans are. Bacteria can spread from one person to another by kissing or sharing toothbrushes and eating utility. Exposure to these bacteria doesn’t mean you will develop gingivitis. However, if you have poor oral hygiene, dry mouth condition, vitamin-C deficiency, or are smoking, you are at increased risk of developing gingivitis.
Babies and children are at increased risk of developing gingivitis because they have an immature immune system. When parents kiss babies on their lips, the gingivitis bacteria (contagious) may spread to the baby’s mouth. According to several studies, babies are more likely to develop gum disease if their parents have it. Avoid kissing others if you have gum disease to prevent the spread of bacteria and visit your dentist for diagnosis and treatment.
How Do You Know You Have Gingivitis?
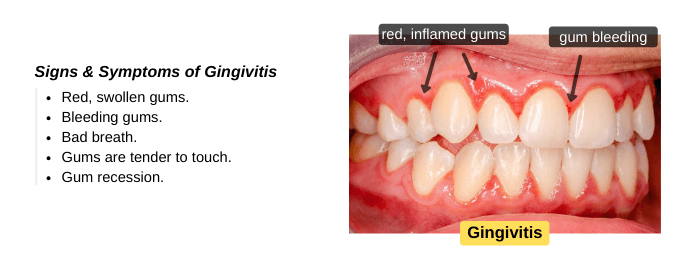
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of gingivitis can help you treat them early and prevent complications. Also, avoid kissing your child if you have these signs and symptoms to prevent the spread of bacteria:
- Red, swollen gums.
- Gum bleeding when brushing or flossing.
- Bad breath.
- Gums are tender to the touch.
- Gum recession.
When You Should Go to the Dentist?
If you noticed any of the previous signs and symptoms, you should schedule an appointment with your dentist. Your dentist will use an ultrasonic scaler to remove plaque and tartar from above and below the gum line. Also, they can identify the underlying cause and treat it. After the cleaning, you should maintain good oral hygiene at home while your gums heal. Your dentist may prescribe antibiotics to help fight infection.
Home remedies can help clear the signs and symptoms of gingivitis, but they have limitations. Home remedies can’t remove tartar from above and below the gum line and can’t treat periodontitis.
How to Prevent Gingivitis & the Spread of Contagious Bacteria?
You can prevent gingivitis by improving your oral health and strengthening your immune system.
- Maintain good oral hygiene: Brush your teeth at least twice daily to remove plaque and gingivitis-causing bacteria from gums and teeth surfaces. Also, use dental floss to remove plaque and food particles between teeth.
- Use fluoride toothpaste: Fluoride toothpaste can help keep your teeth and gums healthy and fight bacteria.
- Don’t share eating utilities or toothbrushes: Avoid sharing toothbrushes, cups, straws, and eating utilities to prevent the spread of gingivitis-causing bacteria, which are contagious.
- Stop smoking: Smoking can weaken your immune system and make it hard for your body to fight infection.
- Eat a healthy diet: Foods rich in fiber, for example, fruits and vegetables, can help keep your teeth and gums clean. Also, they contain nutrients that are essential for the human body.
- Keep your health in check: There is a connection between your oral health and body health. So, visit your doctor to perform a regular check-up and manage existing medical conditions.
- Visit your dentist regularly: Both plaque and tartar irritate the gum tissues. Tartar can’t be removed by brushing or flossing. So, you need to visit your dentist once every six months for professional teeth cleaning.
Is Gingivitis Contagious – Conclusion
Gingivitis itself is not contagious, but the bacteria that cause it are. These bacteria can spread from one person to another through saliva-to-saliva contacts, for example, kissing or sharing toothbrushes, cups, straws, and eating utilities.
Exposure to gingivitis bacteria does not mean that you will develop it, but other factors must be involved, such as poor oral hygiene, dry mouth condition, vitamin-C deficiency, taking certain medications, or being a smoker. So, maintain good oral hygiene and avoid sharing cups, straws, eating utilities, or toothbrushes with others. Also, visit your dentist every six months for regular check-ups and professional teeth cleaning.