Smoking not only has harmful effects on your overall health, but it can also lead to gum disease and other oral problems. Gum disease may not be as serious as lung cancer, but it’s still a big problem. Smoking causes inflammation in the gums, which can lead to tooth loss if not treated. Both smoking and gum disease are linked to serious health problems, such as heart disease. In this article, we’ll take a look at the link between smoking and gum disease, as well as some of the problems that arise from this relationship.
What is Gum Disease?
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a bacterial infection in the gums. It’s an inflammatory condition that affects the gingival tissue and bone supporting the teeth. As it progresses, it can cause serious damage to your jawbone and tooth loss if not treated. Gum disease usually occurs due to poor oral hygiene and the buildup of dental plaque around the teeth. The plaque contains harmful bacteria, which can infect the gums and cause periodontal disease.
We all have harmful bacteria in our mouths at any given time, but when these bacteria are left unchecked, they begin to multiply and cause problems. Smoking allows these harmful bacteria to flourish and get out of control, causing gum disease. Stages of gum disease include:
- Gingivitis: this is the beginning of gum disease, in which inflammation affects only the gingiva. Bleeding occurs when you brush your teeth or floss because the gums are irritated. Learn more about what bacteria cause gingivitis.
- Periodontitis: This is the advanced stage of gum disease, in which the inflammation spreads to deeper tissues in the mouth. Bone loss occurs, and your teeth loosen in their sockets. Learn more about the differences between gingivitis vs periodontitis.
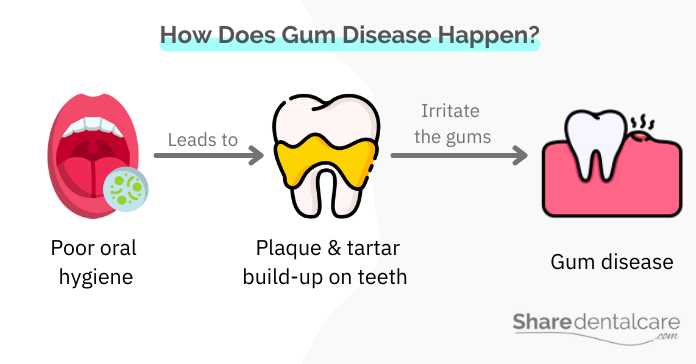
How Smoking and Gum Disease Are Linked?
Smoking has been linked to gum disease for years. It’s one of the most common risk factors for the condition, and smokers are more likely to develop it than nonsmokers.
When you inhale smoke, the chemicals in cigarettes irritate your mouth tissues. Also, smoking can cause dry mouth, which can make it hard for you to fight gum disease since saliva helps wash away food particles and neutralize bacterial acids. A dry mouth allows bacteria in your mouth to grow in number much faster than normal, which increases the risk of tooth decay and gum disease.
In addition, smoking weakens your body’s immune system, which reduces your body’s ability to fight off any infection. If you already have gingivitis or periodontitis, smoking also makes it harder for your gums to heal. Smoking has negative effects on smokers’ teeth and gums.
Some Facts about Smoking and Gum Disease
- Smokers have twice the risk of developing gum disease than nonsmokers.
- The more cigarettes you and the longer you smoke, the greater your risk for gum disease.
- Treatments for gingivitis & periodontitis are less effective for people who smoke.
What Are The Complications of Gingivitis & Periodontitis?
If gum disease is left untreated, it can cause complications such as:
- Persistent bad breath despite having a good oral hygiene
- Pain with chewing.
- Receding gums: Gum tissue pulls away from the teeth, exposing the roots and making your teeth appear longer than usual.
- Periodontal pockets: They are spaces that form between the teeth and gums that bacteria use as a breeding ground.
- Teeth shifting and the spaces between your teeth becoming larger.
- Swollen gums, which may cause aching or bleeding under the gum tissue.
- Gum abscesses.
- The destruction of tooth-supporting tissues and tooth loss.
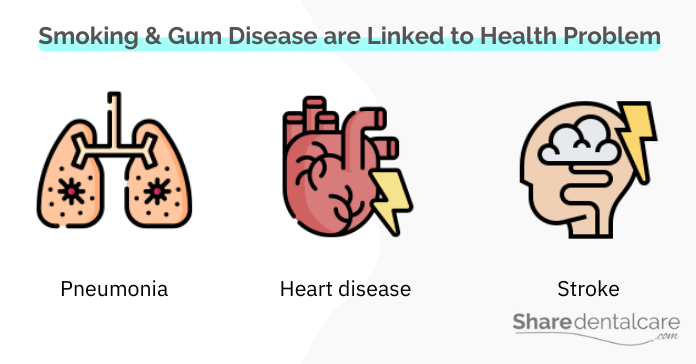
Periodontitis is the most common reason for adult tooth loss. Also, it has been linked to serious health problems, such as heart disease and diabetes.
Both Smoking and Gum Disease are Linked to Serious Health Problems
If you are a smoker and have gum disease, your risk of developing serious health problems is increased. People with gum disease have a 2 – 3 times greater risk of heart attack, stroke, or other serious cardiovascular events than those without gum disease. While smokers have a 4 times greater risk of heart disease and stroke than nonsmokers. Also, research shows that both smoking and gum disease makes it harder for people with diabetes to manage their blood sugar, which can cause complications.
Other Oral Health Problems Associated with Smoking
Other oral health problems can also develop if you smoke. They include:
- Bad breath (halitosis).
- Teeth stains. You can read more about how smoking makes your teeth yellow.
- Reduced sense of taste.
- Dry mouth.
- Dark gums from smoking.
- Tooth decay and cavities.
- Periodontal disease and tooth loss.
- Increased risk of oral cancer.
How To Prevent Oral Health Problems If You Smoke?
The best way to prevent gum disease and other oral health problems is to stop smoking. Stopping smoking will improve your overall health, which in turn will reduce your risk of developing gum disease. If you can’t quit smoking, there are other things you can do to protect your oral health. Here are some tips to prevent oral health problems:
- Quit smoking. If you can’t, smoke in moderation and don’t smoke with others because it increases your exposure to other people’s smoke.
- Brush and floss daily, even if your gums bleed after brushing.
- Use a mouthwash to wash away oral bacteria.
- Eat a healthy diet to provide your body with the nutrients it needs to fight gum disease.
- Drink enough water daily to keep your mouth healthy and help wash away oral bacteria.
- Limit sugary foods and drinks because they’ll increase bacteria in the mouth.
- Visit your dentist for regular checkups and professional cleanings. Also, ask your dentist about other ways to keep your teeth healthy while you are smoking.
While it may seem hard to quit smoking completely, talk to your doctor about nicotine replacement treatments or medication that can help you stop smoking.
Smoking and Gum Disease – Conclusion
Smoking is not only bad for your lungs but also for your oral health. Smokers have twice the risk of developing gum disease than nonsmokers. Also, both smoking and gum disease are linked to serious health problems such as heart disease. If you are a smoker with gum disease, your risk of developing serious health problems is increased. So, it’s important for your oral health and overall well-being to stop smoking or at least smoke in moderation. Besides, maintain good oral hygiene by brushing & flossing your teeth regularly, and visit your dentist for regular professional cleanings. Talk to your dentist about how to quit smoking or deal with your smoking habit.