Gingivitis and periodontitis are both types of gum disease, which is an inflammation of the gums and tissues surrounding the teeth. Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, generally occurs due to bacterial infection. Gingivitis is the early stage of gum disease, and periodontitis is the advanced stage. Gum disease can affect your overall health. According to the NHS, Gum disease can increase the risk of health complications, including stroke, diabetes, and heart disease. Also, It has even been linked with problems in pregnancy and dementia. In this article, we will discuss the difference between gingivitis vs periodontitis.
What is the Difference between Gingivitis vs Periodontitis?
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a bacterial infection that affects the gum tissues and the tooth-supporting tissues. The gum disease can range from mild (gingivitis) to severe (periodontitis). So, what is gingivitis vs periodontitis?
- Gingivitis: it is the early, mild, and beginning form of gum disease that is characterized by redness, swelling of the gums, and gum bleeding. Gingivitis is a reversible condition. It can usually be managed by professional teeth cleaning and oral care at home.
- Periodontitis: it is an advanced stage of gum disease. If gingivitis is left untreated, the infection may spread to the tooth-supporting tissues, causing periodontitis. It is characterized by gum recession, periodontal pockets, dental abscesses, loose teeth, and even tooth loss. Periodontitis can cause permanent damage that can’t be reversed.
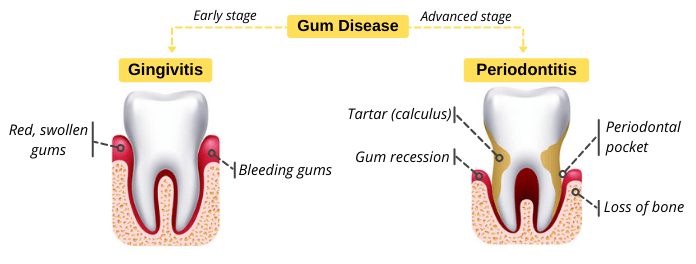
Comparison between Gingivitis vs Periodontitis
This a comparison between gingivitis vs periodontitis. Signs, symptoms, causes, and treatment will be discussed in detail in the following sections.
| Comparison | Gingivitis | Periodontitis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | It is an inflammation of the gum tissues (gingiva). | It is an inflammation of the tooth-supporting tissues such as bone and PDL. |
| Stages of Gum Disease | It is an early stage of gum disease. | It is an advanced stage of gum disease. |
| Signs & Symptoms | Red, swollen gums. Gum bleeding. | Gum recession, periodontal pockets, dental abscess, loose teeth, & tooth loss. |
| Causes | It usually occurs as a result of plaque build-up and poor oral hygiene. | It occurs as a result of untreated gingivitis. The infection spreads to the tooth-supporting tissues. |
| Home Remedies | Home remedies can help treat the signs & symptoms of gingivitis. | Home remedies can’t treat periodontitis. So, you need to visit your dentist immediately to stop its progress. |
| Treatment | Professional teeth cleaning & care at home. | Non-surgical: scaling & root planning. Surgical: flap surgery, soft tissue grafts, or bone grafting. |
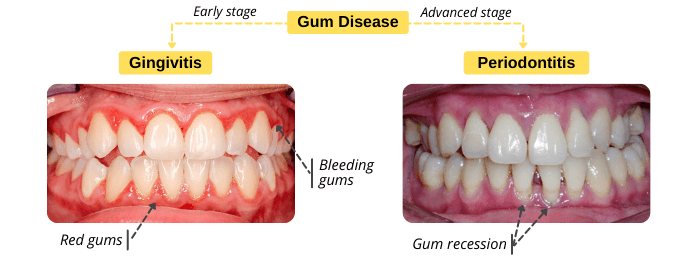
What are the Causes of Gingivitis & Periodontitis?
Gingivitis usually occurs due to plaque build-up on teeth surfaces. Dental plaque is a film of bacteria that forms on your teeth every day. Plaque bacteria decompose carbohydrates in food and produce acids. These bacterial acids irritate the gums, causing gingivitis. Dental plaque can be removed by tooth brushing and flossing. If plaque is not removed regularly, it can harden into tartar. In this case, you will need to visit your dentist to remove the tartar because it can’t be removed by tooth brushing or flossing.
If gingivitis is not treated, the infection can spread to the tooth-supporting tissues, which is known as the periodontium. The tooth-supporting tissues (periodontium) support teeth during their function and maintain them in their places in the upper or lower jawbone. The tooth-supporting tissues include gingiva, jaw bone (alveolar bone), and periodontal ligaments (tissues that attach the tooth to the bone). Read more about “tooth anatomy“. The spread of infection (periodontitis) can cause the destruction of these tissues, which can lead to gum recession, periodontal pockets, tooth mobility, and even tooth loss.
Risk Factors
Having plaque bacteria doesn’t mean you will develop gingivitis. However, if plaque bacteria are present with other factors, this will increase your risk of developing gingivitis and periodontitis. Read more about “is gingivitis contagious?“. You are at higher risk if you have any of these factors because they allow bacteria to grow, and weaken your immune system.
- Poor oral hygiene: if you don’t brush your teeth regularly, plaque and food debris will accumulate on teeth surfaces. This will provide a breeding ground for bacteria to grow.
- Dry mouth condition: saliva plays an important role in oral health. It fights bacteria and neutralizes acids produced by them. The decrease in salivary flow can increase your risk of developing dental caries, gingivitis, and periodontitis.
- Smoking: tobacco chewing and smoking weaken your immune system, and make it harder for your body to fight infection. Also, smoking contributes to dry mouth conditions. Smoking is one of the common causes of gum disease and tooth decay.
- Sugary foods and drinks: bacteria consume carbohydrates in food debris, and produce acids that irritate gums. Sugary foods and drinks provide a breeding ground for bacteria to grow.
- Poor nutrition: a diet that lacks certain nutrients can increase the risk of gingivitis and periodontitis. Vitamins such as vitamin-C are essential for oral health. So, eat a balanced diet that contains fruits and vegetables.
- Broken tooth fillings and braces: food particles and plaque can become trapped in the space between braces and teeth, allowing bacteria to grow. Also, broken tooth fillings can allow plaque and food particles to accumulate between teeth, causing inflammation of the gums.
- Pregnancy: gingivitis and periodontitis may occur during pregnancy or menstrual cycle because of hormonal changes and plaque build-up. Read more about pregnancy gingivitis.
- Age: the risk of periodontitis increases with age. Periodontitis is rare in young people, but they can develop gingivitis.
- Certain medications: taking certain medications can cause the development of gingivitis and periodontitis as a side effect, for example, oral contraceptives, steroids, anticonvulsants, calcium channel blockers, and chemotherapy.
- Some medical conditions: systemic disorders and diseases can weaken your immune system, making it harder for your mouth to fight infection.
How To Recognize Gingivitis vs Periodontitis?
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of gingivitis vs periodontitis can help treat them early and prevent complications. So, what are the signs and symptoms of gingivitis vs periodontitis?
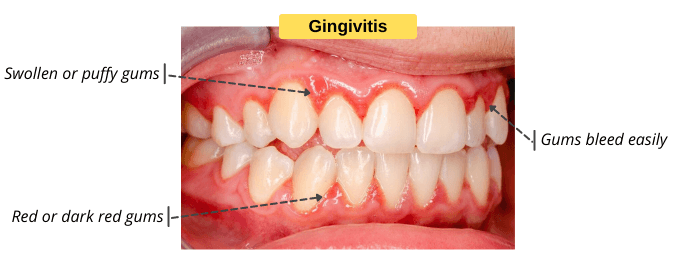
Signs & Symptoms of Gingivitis
- Swollen or puffy gums.
- Red or dark red gums.
- Gums easily bleed when you brush or floss.
- Bad breath.
- Receding gums (mild).
- Gums tender to touch.
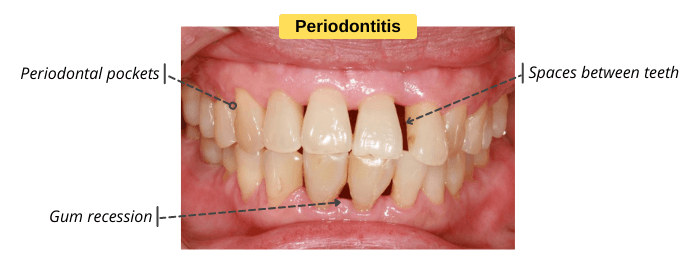
Signs & Symptoms of Periodontitis
- Pain when chewing: this can indicate that the infection spreads to the tooth-supporting tissues.
- Persistent bad breath: the bacteria in the mouth produce sulfur compounds that cause bad breath and unpleasant taste. Find out why you still have bad breath despite maintaining good oral hygiene.
- Gum recession: the gums begin to pull back away from the tooth as a result of the destruction of the supporting bone and periodontal ligaments. The gum recession can’t be reversed. So, you need to visit your dentist to stop its progress.
- Periodontal pockets: they are spaces between teeth and gums. These spaces can accumulate food and plaque, providing a breeding ground for bacteria to grow.
- Dental abscess: the infection can spread to the tooth-supporting tissues, causing a periodontal abscess. Then, the infection can continue to the inner of the tooth, causing a periapical abscess. The treatment includes professional teeth cleaning and root canal treatment.
- Teeth Shifting: periodontitis affects the tooth-supporting tissues such as bone and gum tissues, which can cause teeth movement and the formation of spaces (gaps) between teeth.
- Tooth mobility and even tooth loss: the infection can cause the destruction of supporting bone and tissues that hold teeth in place, which can lead to tooth mobility and loss.
Gum disease doesn’t cause symptoms until the disease is well-established. So, recognizing the signs and symptoms of gingivitis vs periodontitis is important to treat them early, and prevent complications.
Home Remedies for Gingivitis vs Periodontitis
Gingivitis is a reversible condition. Home remedies can help treat gingivitis, but they can’t treat periodontitis. Periodontitis requires immediate treatment at the dental office.
Gingivitis Home remedies
- Saltwater rinses: put ½ teaspoon of salt in a cup of warm water and mix them well. Several studies showed that using salt water can relieve inflammation, help ease pain, and reduce bacteria.
- Brush & floss your teeth regularly: tooth brushing and flossing remove plaque from teeth surfaces and between teeth, which can help reduce gum inflammation and bleeding.
- Use antibacterial toothpaste & mouthwash: they can help fight gingivitis-causing bacteria.
How is Gingivitis vs Periodontitis Treated?
The treatment of gum disease depends on the severity of the disease and the underlying cause.
Treatment of Gingivitis
Gingivitis is a reversible condition. It is usually treated by professional teeth cleaning and treating the underlying cause. At the dental office, your dentist will examine your mouth to identify the underlying cause. Then, they will use an ultrasonic scaler to remove plaque and tartar from above and below the gum line. After that, your dentist will polish your teeth to remove stains and plaque, making your teeth shiny and smooth. Learn more about how is gingivitis treated.
Also, your dentist will treat the underlying causes of gum infection, for example, replacing the broken filling and treating cavities. If gingivitis occurs as a result of systemic disorders or diseases, your dentist will refer you to a specialist.
Treatment of Periodontitis
Periodontitis is an advanced stage of gum disease that can cause irreversible damage. The treatment of periodontitis aims to clean the periodontal pockets, prevent damage of the supporting bone, and stop the progress of the disease. The treatment can be surgical or non-surgical.
Non-Surgical Treatment
If the periodontitis is not advanced, the treatment can include scaling and root planing. Scaling removed tartar and bacteria from tooth surfaces. Root planing smooths the root surfaces to promote healing and the reattachment of the gums to the root surfaces. Your dentist may prescribe antibiotics to help fight the infection.
Surgical Treatment
In the case of advanced periodontitis, the treatment can include oral surgery, for example:
- Flap surgery: your dentist may lift up the gum to expose the roots for more effective scaling and root planing.
- Soft tissue grafts: periodontitis can cause the gum to pull back away from the teeth, exposing the tooth roots. This condition is known as gum recession, which makes the teeth appear longer than normal, and causes an aesthetic problem. Gum recession can’t be reversed. In this case, your periodontist may recommend a soft tissue graft procedure, in which a small amount of tissue is taken from the roof of your mouth (palate) or other sources. Then, your periodontist attaches the tissue to the affected site. Soft tissue grafts can help cover the exposed roots and give your teeth a more pleasing appearance.
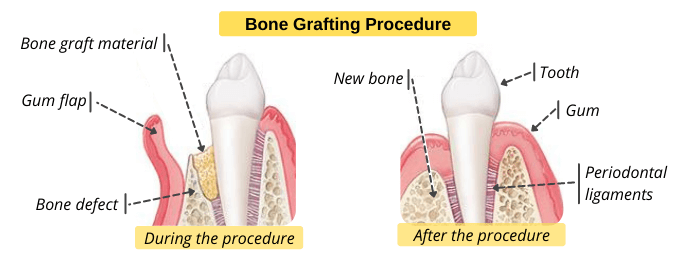
- Bone grafting: periodontitis can cause the destruction of the bone that surrounds teeth, leading to loose teeth and tooth loss. So, your dentist may recommend a bone grafting procedure to prevent bone loss, and promote the regrowth of natural bone. The bone graft can come from different sources such as the patient’s own body or animal source.
How to Protect Your Mouth from Gingivitis & Periodontitis?
If you prevent gingivitis, you will prevent periodontitis. Gingivitis usually occurs as a result of plaque build-up. So, oral hygiene basics can help you treat and prevent gingivitis. Here are some simple ways to help maintain good oral hygiene, and prevent gingivitis or periodontitis.
- Brush and floss your teeth regularly: brush your teeth at least twice daily to remove plaque and food debris from teeth surfaces. Also, use dental floss to remove plaque that accumulates between teeth.
- Stop smoking: chewing tobacco or smoking increases the risk of gum disease because they weaken your immune system, making it harder for your body to fight infection.
- Keep your health in check: visit your doctor if you have a dry mouth or other medical conditions that contribute to gum disease. There is a connection between your oral health and overall health.
- Visit your dentist regularly: visit your dentist every 6 months for regular checkups and professional teeth cleaning. If you are pregnant, visit your dentist in the second and third trimester to prevent pregnancy gingivitis. According to several studies, there is a connection between gum disease and premature birth.