Most adults experience gum infection at least once, but it is less common in children. Poor oral hygiene is one of the most common causes of gum infection, which allows bacteria to grow freely.
Gum disease, also known as gum infection, is a bacterial infection that can damage the gums and tooth-supporting tissues. Healthy gums are firm and usually pink. In gum disease, the gums can become red, inflamed, and swollen and may bleed with brushing or flossing. If left untreated, it can lead to gum recession, loose teeth, and even tooth loss.
The early stage of gum infection, called gingivitis, can be reversed by proper oral hygiene and professional teeth cleaning. However, if gingivitis is left untreated, the infection may spread to the tooth-supporting tissues. This condition is known as periodontitis, an advanced stage of gum disease that can cause tooth loss.
Common Causes of Gum Infection
Poor oral hygiene and smoking are the most common causes of gum infection. However, several other factors contribute to gum infection. Here are seven causes of gum infection:
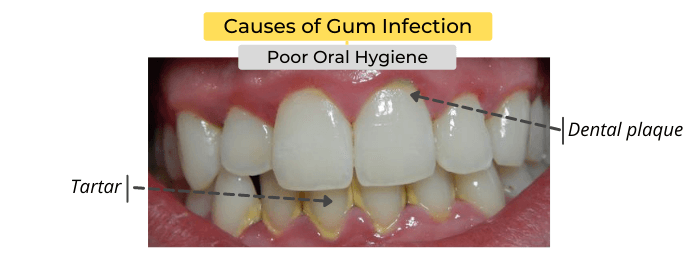
Poor Oral Hygiene / Plaque Buildup
Your mouth is full of different types of bacteria. Not brushing and flossing your teeth allow these bacteria to grow freely. Bacteria can form a thin, sticky film, known as dental plaque, which build-up on your gums and teeth. Gingivitis-causing bacteria in the plaque consume food debris (carbohydrates) and produce acids that attack your teeth and irritate your gums. The gum becomes inflamed, red, and swollen.
Dental plaque can usually be removed by proper oral hygiene such as brushing and flossing. However, if plaque is not removed, it can harden and turn into tartar, which makes it difficult to maintain good oral hygiene. Tartar can only be removed by your dentist. There are several causes of gum infection, and poor oral hygiene is by far the most common.
Smoking & Tobacco Chewing
Smoking and tobacco chewing weaken your immune system, which makes it harder for your body to fight infection. Once you get a gum infection, smoking makes it harder for your gum to heal. Also, smoking causes a dry mouth condition, which promotes bacterial growth. Smoking increases the risk of tooth decay and gum disease.
- Smokers have twice the risk of gum infection compared with non-smokers.
- The longer you smoke, the greater the risk for periodontitis and tooth loss.
- The success rate of the treatment is less in smokers compared with non-smokers.
Hormonal Changes
Hormonal changes during pregnancy, puberty, and the menstrual cycle are one of the common causes of gum infection in women. Hormones are essential for your body’s normal processes. They help with the following:
- Fertility.
- Regular appetite and mood.
- Ensure proper function of organs.
The imbalance of both estrogen and progesterone during puberty, the menstrual cycle, and pregnancy increase the risk of gum infection, which is known as pregnancy gingivitis.
Nutritional Deficiencies
Nutrients you consume have a significant impact on your oral health, such as calcium, phosphorus, vitamin C, vitamin A, and vitamin D. Causes of gum infection include vitamin C deficiency. Vitamin C keeps your gums healthy and protects against gingivitis. Also, it helps strengthen the connective tissues that hold your teeth in place. So, eat foods rich in vitamin C such as citrus fruits, tomatoes, peppers, broccoli, potatoes, and spinach.
Nutritional deficiencies from a poor diet weaken your immune system, making it harder for your body and gums to fight infections.
Dental Problems
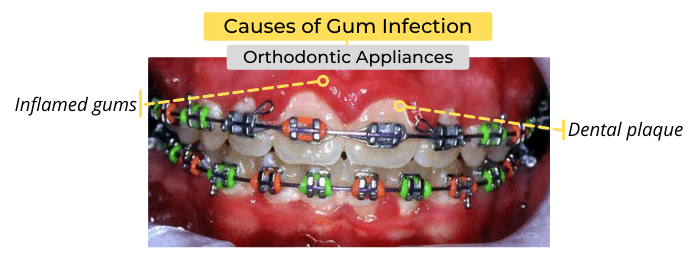
Gum infection causes include crooked teeth, cavities, broken fillings, poorly fitted dentures, and orthodontic appliances. Crooked, misaligned teeth are very common. They can make it difficult to clean your teeth and keep them free of plaque. Also, cavities in between teeth can cause the accumulation of food debris and plaque between teeth, causing gum disease and periodontal pockets.
Dental treatments such as orthodontic appliances, poorly fitted bridges, and dentures can cause gum infections. According to several studies, putting orthodontic appliances on your teeth can cause gum disease because:
- Food debris and plaque can easily be trapped between the appliance and teeth.
- Orthodontic appliances make it harder to clean your teeth.
Also, poorly fitted prostheses such as dentures and bridges allow the accumulation of food debris and plaque between the gums and prostheses. Learn more about oral hygiene with braces.
Some Medications
Gum problems such as inflammation, swelling, and bleeding may occur as a side effect of some medications. For example:
- Oral contraceptives.
- Steroids.
- Anticonvulsants.
- Calcium channel blockers.
- Chemotherapy drugs.
Some medications weaken the immune system, which makes it harder to fight infection. Also, they can decrease the salivary flow and make the mouth dry, which contributes to gum disease.
Medical Conditions
A dry mouth is one of the significant causes of gum infection. Saliva plays an important role in the protection of your teeth and gums. The saliva:
- Washes away food debris that is left on your teeth and gums.
- Neutralizes acids produced by bacteria that irritate the gums.
- Contains minerals that help in the teeth remineralization process.
- Contains antimicrobial agents that fight bacteria.
- Keeps the mouth at a healthy pH balance.
A dry mouth allows bacterial growth and contributes to gum infection. It can occur due to smoking, side effects of some medications, or manifestation of a medical condition/disease. Gum infection may occur as a manifestation of some systemic diseases/conditions such as diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, Crohn’s disease, and HIV/AIDS.
Stop The Causes of Gum Infection, Not Just The Signs
Inflammation of the gums, gum bleeding, and bad breath are the signs of gum infection. So, you need to visit your dentist to identify the underlying causes of gum infection and treat them to prevent complications.
Treatment of Gum Disease
The treatment options vary, depending on the severity of the gum infection and its causes. The treatment includes:
- Professional teeth cleaning (routine cleaning): In the early stage of gum infection, your dentist may recommend professional teeth cleaning to remove plaque and tartar and reverse gingivitis.
- Scaling and root planing (deep cleaning): If the infection spreads to the tooth-supporting tissues, the dentist may perform a deep cleaning to remove subgingival tartar and smooth rough root surfaces.
- Antibiotics: Your dentist may prescribe antibiotics to help control gum bacteria and infection.
- Surgery: In severe cases, your periodontist may recommend oral surgery, such as flap surgery, bone graft, and gum graft, to help restore the damaged tissues.
- Treat dental problems: Treat the underlying causes of gum infection, such as crooked teeth or cavities between teeth.
- Visit your physician: If gum infection occurs as a manifestation of a medical condition/disease or a side effect of some medications, visit your physician to treat the medical condition or change the medication.
Poor oral hygiene and smoking are the most common causes of gum infection. Therefore, you should maintain good oral hygiene and quit smoking to treat gum infections and speed up healing.
To Prevent Gum Infection, You Should:
- Maintain good oral hygiene: Gum infection usually occurs due to poor oral hygiene. So, brush your teeth twice daily with a small, soft toothbrush to remove plaque from gum and teeth. Also, floss your teeth at least once per day to remove plaque and food debris from between teeth. If you have braces, brush your teeth 5 times a day.
- Quit smoking: Smoking and tobacco use are some of the most significant causes of gum infection. They also cause dry mouth conditions and make gum treatment less effective.
- Eat a well-balanced diet: Drink plenty of water and eat a balanced diet rich in vitamin C.
- Visit your dentist regularly: Visit your dentist at least once every 6 months for professional teeth cleaning to remove plaque and tartar. If you are pregnant, schedule regular dental appointments for check-ups and professional teeth cleaning.
Causes of Gum Infection – Conclusion
Healthy gums are firm and usually pink. Gum disease, gum infection, is a bacterial infection that can make the gums red, inflamed, swollen, and bleed with brushing or flossing. If left untreated, the infection may spread to the tooth-supporting tissues and cause tooth loss.
Poor oral hygiene and smoking are the most common causes of gum infection. Other causes may include hormonal changes during pregnancy, vitamin D deficiency, side effects of some medications, and medical conditions. To prevent gum infection and keep healthy gums, brush and floss your teeth regularly and visit your dentist at least once a month for professional teeth cleaning.