Periodontal disease is a bacterial infection of the tissues that support your teeth, including gums and bones. With time, the infection can cause bone loss and tooth loss. Periodontal disease can be reversed in the early stages, but if it’s left untreated, it can cause permanent damage. To prevent periodontal disease from progressing, you must maintain good oral hygiene habits such as brushing and flossing your teeth regularly. In this blog post, we will discuss what is periodontal disease, its stages, and reversing bone loss.
What’re Periodontal Disease & Its Stages?
Before we discuss reversing bone loss, it’s important to know what is periodontal disease. Periodontal disease is a bacterial infection of the gums caused by plaque (a sticky, colorless film of bacteria). Plaque bacteria break down the food particles in your mouth, producing acids that can damage the tooth enamel and irritate the gums. If plaque is not removed regularly with brushing and flossing, it can harden into tartar (a yellowish, calculus deposit). Tartar can’t be removed with brushing and flossing, so you will need to see a dentist for a professional cleaning.
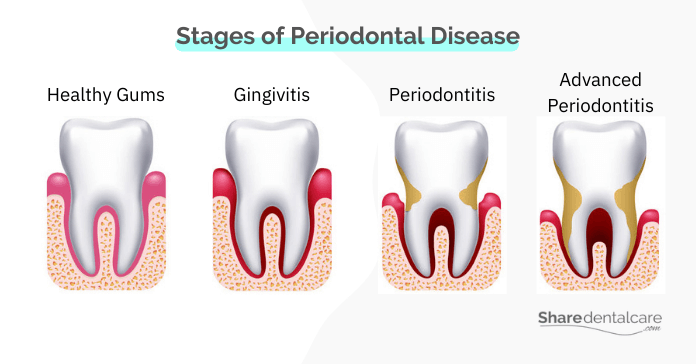
Stages of Periodontal Disease
The stages of periodontal disease are:
- Gingivitis: gingivitis infection is the mild form of periodontal disease and the most common form in adults and adolescents over age 12. In this stage, the gums become swollen, red, tender, and bleed easily during brushing and flossing.
- Periodontitis: If gingivitis is not treated, it can progress into periodontitis. In this stage, the infection moves down below the gum line and destroys the bone and fibers that hold your teeth in place, causing irreversible damage. The gums may pull away from the teeth, creating pockets of infection. In this stage of periodontal disease, visit your dentist to reverse the bone loss to prevent tooth loss.
- Advanced Periodontitis: In this final and most severe stage of periodontal disease, the infection destroys the bone and tissue that holds your teeth in place, causing loose teeth and tooth loss. Reversing bone loss may or may not work at this stage of periodontal disease.
You can read more about the difference between gingivitis vs. periodontitis.
Symptoms of Periodontal Disease Bone Loss That Needs Reversing
In the early stage, periodontal disease usually causes no pain. You may not even know you have it. In the case of gingivitis, you may experience the following signs and symptoms:
- Red, swollen gums.
- Gum bleeding when brushing or flossing.
- Bad breath that doesn’t go away, despite maintaining good oral hygiene.
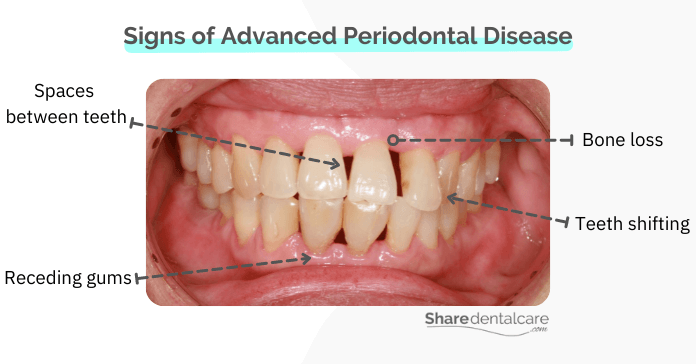
As periodontal disease worsens, there are a few signs and symptoms you should be aware of because it means that the infection begins to destroy the bone holding your teeth in place. At this stage of periodontal disease, reversing bone loss may be necessary.
- Gum recession: the gums may pull away from the teeth, making them appear longer than usual.
- Periodontal pockets: these are spaces between the teeth and gums that become infected. Read more about deep pockets between teeth.
- Teeth shifting: the teeth may move from their original position.
- Change in the bite: the teeth may not fit together properly when you close your mouth.
- Gum abscess: a pocket of pus and bacteria from an infection in the gums.
- Loose teeth: If the bone and fibers holding your teeth in place have been destroyed, they may become loose.
- Tooth loss: If the infection is not treated, it can cause permanent tooth loss.
If you have any of these signs, visit your dentist to reverse the bone loss as soon as possible to prevent tooth loss and further damage.
Treatment Options for Periodontal Disease & Reversing of Bone Loss
There are many ways to treat periodontal disease, depending on its severity. In the early stages of periodontal disease, reversing bone loss may not be necessary. Gingivitis is usually treated with professional teeth cleaning every three to six months, as well as good oral hygiene habits. Read more about how gingivitis is treated.
In mild to moderate cases of periodontitis, your dentist may recommend scaling and root planing, which is a deep-cleaning procedure to remove the plaque and tartar from below the gum line. Also, they will prescribe antibiotics and other medications to control the infection.
If you’re experiencing advanced periodontitis, a few possible treatments include:
- Flap surgery: the gums are lifted and separated from the teeth for more effective scaling and root planing.
- Pocket reduction surgery: to reduce the depth of the periodontal pockets.
- Gum grafts: The procedure involves taking a piece of healthy gum tissue from another part of your mouth and using it to cover the exposed root surfaces.
- Bone grafting: This procedure involves using small fragments of bone (your own, synthetic, or donated) and grafting it to the area where the bone has been lost.
Reversing Advanced Periodontal Disease with Bone Loss
If you have advanced periodontal disease with bone loss, your dentist may recommend surgery and a bone grafting procedure for reversing the bone loss. This surgery may involve flap surgery, in which the gums are lifted up to remove the plaque and tartar from below the gums. Also, the dentist will perform scaling and root planing to remove tartar and clean the affected areas. Then, a bone graft procedure will be performed to help rebuild the lost bone. After the surgery, you should follow your dentist’s instructions and improve your oral hygiene habits to ensure proper healing.
In severe cases of periodontal disease with bone loss, reversing the bone loss may not be a possibility because the bone may be too damaged. In these cases, your dentist may recommend tooth extraction and a dental implant or to replace the missing tooth.
Reversing Periodontal Disease Bone Loss – Conclusion
Periodontal disease is a bacterial infection of the gums that can cause damage to the tooth-supporting tissues and tooth loss if not treated. There are many ways to treat periodontal disease, depending on its severity. If you have advanced periodontal disease, your dentist may recommend flap surgery, scaling & root planing, and a bone grafting procedure for reversing the bone loss and preventing tooth loss.
If the damage is too severe, reversing the bone loss may not be possible, and your dentist may recommend a tooth extraction. Visit your dentist to determine the severity of periodontal disease and the best treatment option suitable for you.