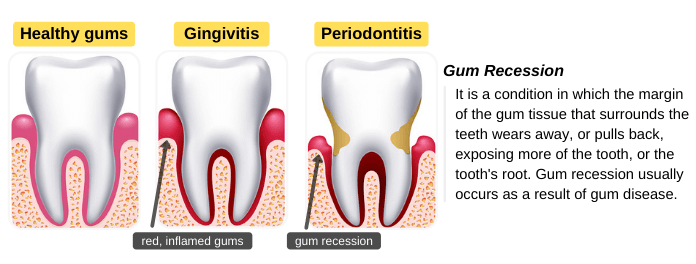
Healthy gums fit tightly around your teeth. Gum recession, also known as gingival recession, is a condition in which the gum margin pulls back, exposing the tooth’s root. It usually occurs as a result of periodontitis, an advanced stage of gum disease. It is a common problem, but most people don’t recognize it because it progresses gradually and causes no pain in the early stages.
Gum recession can cause an aesthetic problem because it makes the teeth appear longer than usual, especially anterior teeth. You can treat gum recession at an early stage and stop their progress. However, if left untreated, the infection may spread to the tooth-supporting tissues, causing complications such as tooth sensitivity, pain, periodontal pockets, tooth mobility, and tooth loss.
How Does Gum Recession Occur?
Poor oral hygiene leads to the accumulation of dental plaque and tartar on teeth surfaces. Dental plaque is a film of bacteria that decompose carbohydrates and produce toxins. Plaque can easily be removed by tooth brushing and flossing.
If plaque is not removed regularly, it hardens into tartar, which can’t be removed by toothbrushing. Both plaque and tartar irritate gums, causing gingivitis (the beginning of gum disease). Gingivitis can be reversed by professional teeth cleaning and improving oral hygiene habits.
However, if gingivitis is left untreated, the infection of the gums may spread to the tooth-supporting tissues, causing periodontitis. Healthy gums fit tightly around your teeth and protect them. In periodontitis, the gum margin begins to pull back, exposing the tooth’s root.
Signs & Symptoms of Gingival Recession
Gingival recession is a symptom of gum disease. Most people are not aware that they have gum recession because it progresses gradually and causes no pain in the early stage. The following signs and symptoms may indicate that you have gum disease and gingival recession:
- Red, swollen gums: the gums are inflamed and tender to the touch.
- Gum bleeding: this may occur due to the accumulation of plaque and tartar below the gumline.
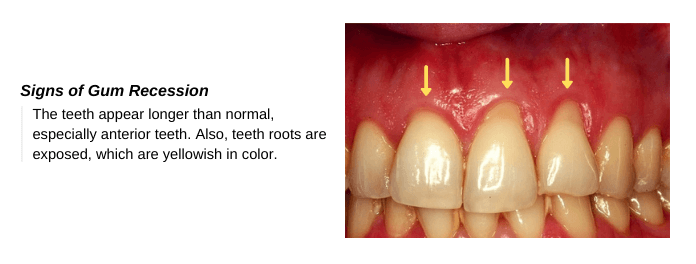
- Teeth are long: you may notice that the teeth are longer than usual, especially the anterior teeth.
- Exposed roots: tooth roots are yellowish in color and more sensitive than tooth enamel. If you noticed the exposed tooth’s root or sensitivity to hot or cold, you should visit your dentist immediately for diagnosis and treatment.
- Periodontal pocket: the inflammation and swelling can cause the gums to pull away from your teeth, forming a space between the teeth and the gums. These spaces are known as periodontal pockets. These pockets accumulate plaque and food debris.
- Loose Teeth: It is an advanced sign of receding gums, which indicates severe damage to the tooth-supporting tissues.
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of gum disease will help you treat it early and prevent complications. You can read more about the early signs and symptoms of gingivitis.
Causes & Risk Factors for Gum Recession
Gum recession usually occurs as a result of periodontitis, an advanced form of gum disease. Several factors can increase your risk for gum disease and gingival recession, including:
- Poor oral hygiene: the accumulation of plaque and tartar on teeth surfaces can cause receding gums.
- Smoking or chewing tobacco: smoking weakens your immune system and makes it harder for your body to fight infection. Smoking is one of the most common risk factors for gum disease.
- Wrong toothbrushing technique: using a hard-bristled toothbrush or the wrong brushing technique can damage the gums, leading to receding gums.
- Hormonal changes: for example, during pregnancy and the menstrual cycle.
- Dry mouth condition: it increases the risk of gum recession.
- Age: The risk of receding gums increases with age. According to the CDA, receding gums occurs in adults 40 years or older.
- Medications: some medication that causes dry mouth as a side effect, for example, anti-convulsants, hypertensive medications, and chemotherapy drugs.
- Medical conditions: The risk of receding gums may increase with some medical conditions such as diabetes mellitus and HIV.
- Misaligned teeth: they accumulate plaque and tartar more rapidly than well-aligned teeth. Also, it is difficult to clean misaligned teeth, which increases the risk of receding gums. Besides, the wrong distribution of bite force can cause damage to the tooth-supporting tissues and recession.
- Teeth grinding and clenching: the excessive force on the teeth can destroy the tooth and its supporting tissues, which can lead to tooth wear, tooth fracture, sensitivity, receding gums, tooth mobility, and tooth loss.
- Injury: trauma to the gums during a fall, playing a contact sport, or other accident may cause receding gums.
Can Gums Grow Back?
Receding gums don’t grow back because gum tissue doesn’t regenerate like other types of tissues, for example, skin tissues. However, you can prevent the problem from getting worse and repair gum recession by visiting a periodontist.
Complications of Gum Recssion
Ignoring the symptoms of gum disease and gingival recession can lead to:
- An aesthetic problem because the receding gums make the teeth appear longer than usual.
- Pain and tooth sensitivity.
- Root caries as a result of the exposure of roots.
- Dental abscess due to the spread of infection.
- Tooth loosening and eventually tooth loss.
How Gum Recession is Treated?
The treatment aims to stop the gum disease from getting worse and repair gum recession.
Scaling & Root Planning (Deep Cleaning)
Your dentist will use a scaler to remove the plaque and tartar from above and below the gum line to stop the progression of gum disease. Also, they will smooth out your teeth roots to:
- Make it difficult for bacteria to attach themselves, and
- Help your gums reattach to your teeth.
The deep cleaning may be performed under local anesthesia and may require more than one visit to the dentist. Also, your dentist may recommend orthodontic treatment if receding gums occur due to misaligned teeth.
Flap Surgery
In severe cases, your periodontist may recommend flap surgery. In this procedure, the periodontist lifts up the gums to perform a more effective scaling and root planing. Then, they suture the gums back in place.
Bone & Gum Graft Surgery
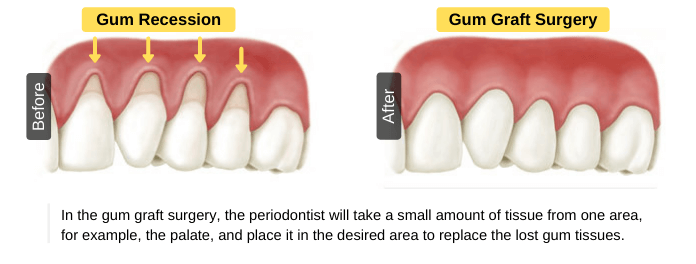
The purpose of this procedure is to repair gum recession by replacing the lost gum or bone tissues. In gum graft surgery, the periodontist will take a small amount of tissue from one area, for example, the palate, and place it in the desired area to replace the lost gum tissues. Receding gums may occur as a result of the loss of supporting bone. So, your dentist may recommend a bone graft surgery, which involves the placement of either synthetic particles or a piece of bone to help the supporting bone grow back
Gum tissue grafts are effective at repairing gum recession. However, this won’t prevent the development of the problem in the future. So, you have to maintain good oral hygiene at home and visit your dentist for regular dental checkups.
Prevention of Gum recession
Prevention of gum recession is better than treatment because receding gums won’t grow back, causing a permanent aesthetic problem. These tips will help you prevent gum recession:
- Practice good oral hygiene: brush your teeth at least twice per day, and floss your teeth at least once per day. Practice oral hygiene basics daily.
- Use the right toothbrush: choose a soft-bristled toothbrush with a size and shape that allows access to all parts of the mouth. Also, replace your toothbrush every 2-4 months.
- Use fluoride toothpaste & antiseptic mouthwash: to help fight plaque bacteria.
- Follow the right brushing technique: brushing your teeth aggressively or following the wrong brushing technique can lead to gum recession.
- Wear a mouthguard: If you have a teeth-grinding, wear a mouthguard to prevent the destruction of tooth-supporting tissues.
- Visit your dentist regularly: schedule an appointment with your dentist for a regular check-up and professional teeth cleaning.
Conclusion
Gum recession, also known as gingival recession, is a condition in which the gum margin pulls back, exposing the tooth’s root. It usually occurs as a result of periodontitis, an advanced stage of gum disease. Poor oral hygiene is the most common cause because it allows the accumulation of plaque on teeth and the growth of bacteria in the mouth. Other causes may include wrong tooth brushing technique, teeth grinding, and misaligned teeth.
Receding gums don’t grow back because gums don’t regenerate like other types of body tissues. Treatment aims to stop the progression of gum disease and repair receding gums. The treatment includes deep cleaning, flap surgery, and bone & gum graft surgery, depending on the severity of the gum recession. Prevention is better than treatment so, practice good oral hygiene and visit your dentist regularly.