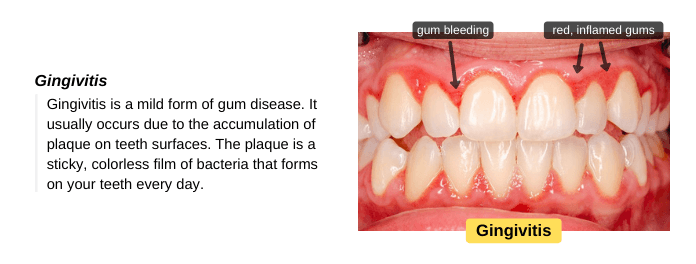
Gingivitis is a bacterial infection of the gums that usually occurs due to the build-up of dental plaque on teeth, a sticky, colorless film of bacteria. These bacteria produce toxins that irritate the gums, causing inflammation, redness, and swelling. If your gums bleed easily with brushing or flossing, you may have gingivitis. Gingivitis can be easily treated by professional teeth cleaning and improving oral hygiene. However, if left untreated, the infection may spread to the tissues supporting your teeth and cause tooth loss. So, visit your dentist for diagnosis and treatment.
Signs and Symptoms
If you notice any of the following signs and symptoms, visit your dentist as soon as possible to get gingivitis treated and avoid complications. The signs and symptoms of gingivitis include:
- Red, swollen gums.
- Gums bleed easily, especially with brushing and flossing.
- Bad breath.
- Gums tender to touch.
- Receding gums. The teeth may appear longer, especially the anterior teeth.
Causes of Gingivitis
Gingivitis usually occurs due to the build-up of dental plaque on teeth surfaces, a sticky, colorless film of bacteria. These bacteria produce acids that irritate the gums, causing inflammation and swelling. If plaque is not removed regularly by brushing and flossing, it will harden into tartar, which is difficult to remove. So, visit your dentist for professional teeth cleaning to remove plaque and brown tartar on your teeth.
Gingivitis can be easily treated by professional teeth cleaning and improving oral hygiene. However, if left untreated, the infection may spread to the bone and tissues supporting your teeth, causing permanent damage, such as tooth loss.
Risk Factors
Several factors can increase your risk of developing gingivitis, such as:
- Poor oral hygiene: Not brushing or flossing your teeth is the most common cause of gingivitis. Poor oral hygiene leads to the build-up of plaque on teeth surfaces. If you don’t remove plaque by brushing or flossing, it will harden into tartar. Both plaque and tartar irritate gums and cause gingivitis, which needs to be treated immediately to avoid complications.
- Smoking and chewing tobacco: It causes dry mouth conditions, which increases the risk of gum disease. Smoking causes gum disease & tooth decay.
- Dry mouth condition: It may occur as a result of dehydration, smoking, a side effect of some medications, chemotherapy, and radiotherapy to the head and neck.
- Broken restoration & poorly fitted crowns: These cause the accumulation of plaque more rapidly and make it difficult to clean.
- Poor nutrition: Vitamin C plays a vital role in the gum’s health.
- Hormonal changes: During pregnancy (pregnancy gingivitis), menstrual cycle, or use of birth control pills.
- Some medical conditions: Medical conditions such as diabetes mellitus, viral infections, & fungal infections may increase the risk of gingivitis.
If you noticed that your teeth appear longer than usual, this means that gingivitis needs to be treated immediately.
How is Gingivitis Diagnosed?
To get gingivitis treated early, it should be diagnosed early. So, you should visit your dentist immediately if you notice any signs and symptoms of gingivitis to get it treated and avoid its progression to periodontitis. Methods of diagnosis include:
- Oral Examination: Your dentist will use a mirror and probe to examine your oral cavity.
- Medical history: They will ask you about your medical history and any medications you take. Gingivitis is sometimes associated with some medical conditions and may occur as a side effect of some medications.
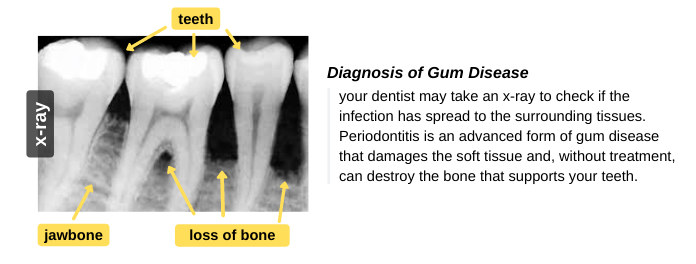
- X-ray: Your dentist may take an x-ray to check if the infection has spread to the surrounding tissues. The spread of infection may cause a breakdown of the surrounding bone and periodontal ligaments (PDL). You can read more about “tooth anatomy” to know the structure of teeth and surrounding tissues.
How is Gingivitis Treated?
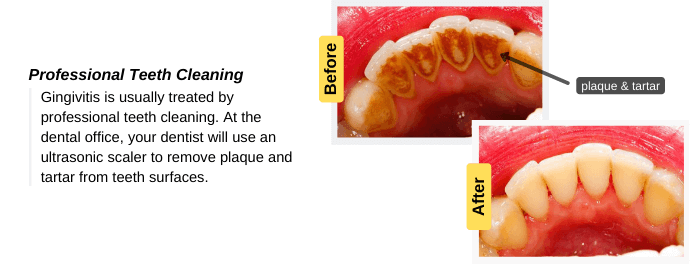
Gingivitis is usually treated by removing dental plaque and tartar. Plaque and tartar produce toxins that irritate healthy gums and cause gingivitis. We will discuss in detail how gingivitis is treated at the dental office and at home.
How is Gingivitis Treated in the Dental Office?
At the dental office, your dentist will use an ultrasonic scaler to remove plaque and tartar from teeth surfaces. Also, your dentist will polish your teeth to make them smoother. You have to visit your dentist to get gingivitis treated properly. Also, your dentist will replace broken tooth fillings and poorly fitted crowns and bridges.
How is Gingivitis Treated at Home?
These instructions will help you reduce the signs and symptoms of gingivitis, but they won’t eliminate the need for a visit to the dentist to remove the underlying cause. Also, you should follow these instructions after gingivitis gets treated to prevent its recurrence.
- Brush your teeth regularly: Brush your teeth with a soft-bristled toothbrush for 2 minutes, at least twice daily. Also, follow the proper tooth-brushing technique to prevent damage to the gingiva.
- Floss your teeth: A toothbrush can’t remove plaque from between teeth. So, floss your teeth at least once daily to remove plaque from between teeth.
- Use fluoride toothpaste and antibacterial mouthwash: They can help fight plaque bacteria. Note: don’t use mouthwash immediately after toothpaste because mouthwash can wash away the concentrated fluoride in toothpaste. So, wait a while before using mouthwash.
Can Gingivitis be Treated by Medications?
No medication can cure gingivitis, but your dentist may prescribe medications as a part of the treatment to help control infection. Medications include an antiseptic chip, antibiotic gel, and oral antibiotics (in the case of serious infection). Also, your dentist may prescribe an antimicrobial mouthwash to use as a part of your daily oral hygiene routine to help control gingivitis bacteria.
What Happens if Gingivitis is not Treated?
If gingivitis is not treated early, the infection may spread to the surrounding tissues, causing complications such as:
- Gum recession: The margin of gums that surrounds the tooth pulls back, exposing the tooth’s root. The teeth may appear longer than usual, which causes an aesthetic problem.
- Periodontitis: It is an advanced form of gum disease. The spread of infection to the tooth-supporting tissues may lead to the breakdown of bone and periodontal ligaments (PDL).
- Gum abscess: The spread of infection to the tooth-supporting tissues may cause a gum abscess, which may lead to a periapical abscess. In this case, the affected tooth may need root canal treatment.
- Tooth mobility and tooth loss: If gingivitis is not treated, this will cause the destruction of the supporting bone and periodontal ligaments, which will eventually lead to tooth mobility and tooth loss.
Several studies have linked gum disease to systemic problems such as cardiovascular disease (heart attack or stroke), diabetes mellitus, and lung disease risk.
Prevention
Gingivitis can be easily treated and prevented. You just have to maintain good oral hygiene. Follow these instructions to get healthy gums and prevent gingivitis:
- Brush and floss your teeth regularly: brush your teeth twice daily to remove dental plaque from teeth surfaces. Also, remember to use dental floss to remove plaque that accumulates between teeth.
- Eat nutrient-rich foods: vitamin C is important to get healthy gums.
- Avoids foods high in sugar: plaque bacteria feed on sugars in food and produce toxins that irritate gums and cause cavities.
- Visit your dentist or oral hygienist regularly: visit your dentist at least once every 6 months for professional teeth cleaning and to get gingivitis treated early before it causing any complications.
How is Gingivitis Treated – Conclusion
Gingivitis is a mild form of gum disease caused by the build-up of plaque on teeth, a sticky, colorless film of bacteria. These bacteria produce acids that irritate the gums, causing inflammation, redness, and swelling. If left untreated, the infection may spread to the bone and tissues supporting your teeth, causing tooth loss.
Gingivitis is usually treated by professional teeth cleaning and improving oral hygiene. During the treatment, the dentist uses a scaler to remove plaque and tartar from teeth surfaces and polishes your teeth to make them smoother. Also, you need to maintain good oral hygiene after treatment to prevent the recurrence of gingivitis.