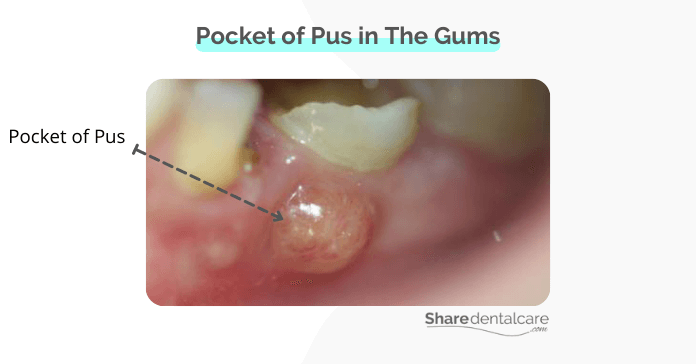
If you have a pocket of pus in your gums, it may be a sign of a dental abscess, which is a bacterial infection. Dental abscesses can be painful and, if left untreated, can lead to serious health complications. In this blog post, we will discuss the causes and symptoms of dental abscesses, as well as treatment options.
Why I Have a Pocket of Pus in The Gums?
A pocket of pus in the gums is a sign of a dental abscess. A dental abscess is a collection of pus that is caused by a bacterial infection. The pus is a yellowish-white, thick fluid that contains bacteria and white blood cells. The pocket of pus on the gums can occur in both adults and children.
Dental abscesses can be painful and, if left untreated, can lead to serious health complications. That’s why it’s important to see a dentist if you think you may have one.
Types of Dental Abscess
The pocket of pus can develop in different parts of the mouth, for example, at the end of the tooth or in the gums surrounding a tooth. Depending on the location, a dental abscess can be classified as:
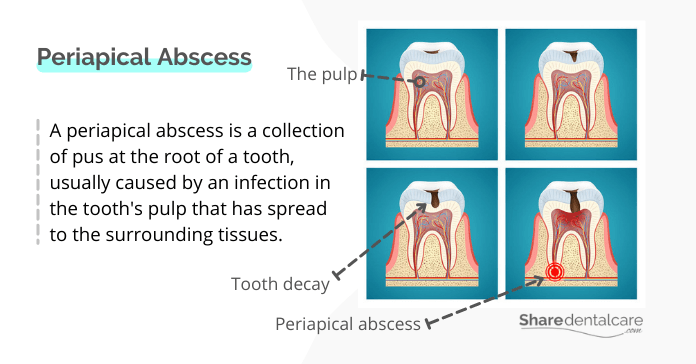
- Periapical abscess: it is the most common type of dental abscess. The periapical abscess occurs at the tip of a tooth’s root due to an infection in the tooth’s pulp (the innermost layer that contains blood vessels and nerves).
- Periodontal abscess: This type of dental abscess occurs in the gum tissue near the tooth root due to an infection in the periodontium – tissues that surround and support the tooth.
- Gingival abscess: This type of abscess occurs in the gum tissue near the tooth crown when a foreign body, such as a food particle, gets stuck between the gum and tooth.
- Pericoronal abscess: this type occurs due to the infection of an operculum covering a wisdom tooth. The operculum is a flap of gum tissue that forms over a partially erupted or impacted tooth.
All these types can cause the formation of a pocket of pus in the gums.
What Causes The Formation of a Pocket of Pus in The Gums?
The formation of a pocket of pus in the gums occurs as a result of bacterial infection. However, how this occurs depends on the type of abscess.
- Periapical abscess: This type of abscess is usually the result of an infection in the pulp (the inner part of the tooth that contains nerves and blood vessels). The infection occurs when bacteria enter the pulp through a crack or cavity in the tooth.
- Periodontal abscess: This type usually occurs as a result of periodontitis, a severe form of gum disease. The pocket of pus occurs when bacteria enter the gums through a pocket (a space that forms between the tooth and the gum tissue).
- Gingival abscess: This type occurs when a foreign body, such as a toothbrush bristle, gets stuck in the gums.
Symptoms Associated With a Pocket of Pus
The pocket of pus in the gums is usually accompanied by other symptoms, such as:
- Severe toothache
- Pain when chewing
- Sensitivity to hot and cold temperatures
- Swelling in the gum
- Redness in the gum
- Bad taste in the mouth
- Bad breath
If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s important to see a dentist as soon as possible.
Treatment of a Pocket of Pus in The Gums
The treatment of the pocket of pus in the gums depends on the underlying cause. The treatment includes:
- Removal of the foreign body: If the pocket of pus is caused by a foreign body (gingival abscess), your dentist will remove it. Then, the pocket will be cleaned and rinsed with a sterile solution. Also, the dentist will recommend professional teeth cleaning.
- Antibiotics: your dentist may prescribe antibiotics to help control the infection.
- Root canal treatment: If the pocket of pus is the result of an infection in the tooth pulp (periapical abscess), your dentist may recommend a root canal to remove the infected tissue. The procedure involves the removal of the tooth pulp and the cleaning of the root canal. Then, your dentist will fill the root canal with a filling material.
- Scaling and root planing: If the pocket of pus in the gums occurs as a result of periodontitis (periodontal abscess), your dentist may recommend a procedure called scaling and root planing. This involves removing the tartar and bacteria from above and below the gumline. If the periodontal infection spreads to the tooth pulp, your dentist may also recommend a root canal.
- Operculectomy: It is a surgical procedure that involves the removal of the gum tissue flap covering a partially erupted or impacted tooth.
- Tooth extraction: In some cases, your dentist may recommend extracting the tooth if it’s too damaged to be saved.
Complications of Untreated Pocket of Pus in The Gums
The pocket of pus in the gums is a serious condition that can lead to complications if it’s not treated promptly. The potential complications include:
- Tooth loss: the dental abscess can destroy the bone around the tooth (alveolar bone), which can lead to tooth loss.
- Spread of the infection: the infection can spread to other parts of the body, such as the jawbone, the neck, and even the brain.
- Sepsis: it is a life-threatening condition that occurs when the body’s response to an infection causes inflammation throughout the body.
If you think you have an abscess in your gums, it’s important to see a dentist as soon as possible. Early treatment can help prevent complications.
Conclusion
The presence of a pocket of pus in the gums is a sign of a dental abscess. This condition is caused by a bacterial infection. If it’s not treated promptly, it can lead to complications, such as tooth loss and the spread of the infection. The treatment depends on the underlying cause. In the case of periapical abscesses, the dentist may recommend a root canal treatment while for periodontal abscesses, the dentist may recommend scaling and root planing. If the tooth is severely damaged, the dentist may recommend extracting it. If you have a pocket of pus in your gums, visit your dentist as soon as possible. Early treatment can help prevent complications.