A gum abscess is a collection of pus that forms in the gum. It is caused by a bacterial infection. Gum abscess may cause persistent pain, swelling, and other symptoms. Also, the pain may radiate to other areas, for example, the ear, jaw, and neck. If you have gum abscess, visit your dentist as soon as possible. Your dentist will eliminate the infection and relieve the pain. Untreated gum abscess can spread to other parts of the body, leading to serious, even life-threatening complications. In this article we will discuss:
- What are the signs and symptoms?
- How to control pain?
- Will a gum abscess go away on its own?
- How is a gum abscess is treated?
- How do you know if a gum abscess has spread?
The Periodontium: The Tissues that Surround and Support the Tooth
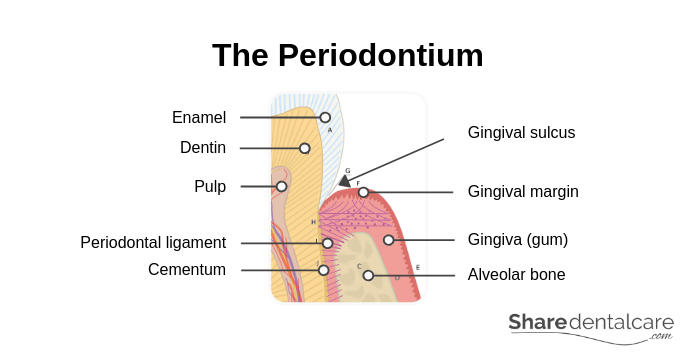
In order to understand gum abscess, it is important to know the structure of the periodontium, the tissues that surround and support the tooth. The periodontium includes gingiva (gum), periodontal ligament (PDL), cementum and alveolar bone.
- Gingiva (gum): it is the part of oral mucosa that covers the upper and lower jaw, and surrounds the teeth. It is the only visible part of the periodontium.
- Periodontal ligament (PDL): it is a group of connective tissue fibers that support and attach the tooth to the alveolar bone. Aso, it allows for minor movement of the tooth in its socket without damaging the tooth and surrounding tissues.
- Cementum: it covers the roots of the tooth and attaches the tooth to the alveolar bone by anchoring the periodontal ligament.
- Alveolar bone: it is the bone that supports and holds teeth. Alveolar bone is covered by the gingiva.
Types of Gum Abscess
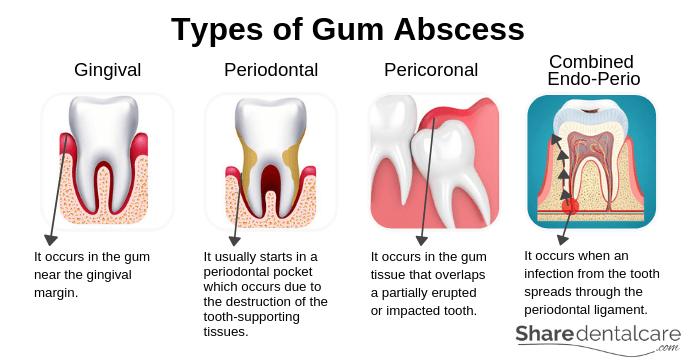
There are several types of abscess that can occur in the gum and surrounding tissues. Each type occurs in a different place for a different reason.
- Gingival abscess: this type occurs in the gum near the gingival margin, the most coronal part of the gum. Gingival abscess doesn’t affect the tooth or tissues that support the tooth (the periodontal ligament).
- Periodontal abscess: it is usually associated with advanced gum disease. A periodontal abscess usually starts in an infected periodontal pocket which occurs due to the destruction of the tooth-supporting tissues (alveolar bone and periodontal ligament). Sometimes, the infection from the periodontal pocket spreads into the tooth, causing the death of the pulp and formation of abscess at the root tip (periapical abscess).
- Pericoronal abscess: this type occurs in the gum tissue that overlaps a partially erupted or impacted tooth.
- Combined Endo-Perio lesion: this type occurs when an infection from the tooth (periapical abscess) spreads through the periodontal ligament.
Symptoms of Gum Abscess
Gum abscess may cause persistent, severe pain. Also, you may notice redness and swelling of the gum in the affected area. Other signs and symptoms of gum abscess include:
- Persistent, throbbing pain in the affected area. Sometimes, the pain may spread to your ear, jaw, and neck.
- The pain gets worse when you bite or chew on the affected area.
- Tooth mobility.
- Swelling and redness of the gum.
- Pus discharge and a foul taste in the mouth.
- Tenderness of the lymph nodes under the jaw.
- Fever.
- Sensitivity to heat or cold foods and drinks.
Relieving Gum Abscess Symptoms
Gum abscess usually causes persistent, sever pain that can radiate to your ear, jaw, and neck. So, you may need over-the-counter (OTC) painkillers such as ibuprofen, paracetamol, and aspirin to relieve the pain until you are able to see your dentist. First, consult your doctor or pharmacist if you:
- Are pregnant or breastfeeding.
- Have an allergic reaction from taking painkillers.
- Are taking medications that may interfere with painkillers.
- Have health problems, for example, asthma, high blood pressure, stomach ulcer, history of stomach problems, liver disease, or kidney disease.
Aspirin is not suitable for children under the age of 18 years old because it increases the risk of Reye’s syndrome. Before taking OTC painkillers, consult your doctor or pharmacist.
Home Remedies to Control the Pain
These home remedies may help you control the pain until you are able to see your dentist:
- Avoid chewing or biting on the affected side.
- Try to eat soft foods.
- Avoid hot or cold foods and drinks if they make the pain worse.
- Use a soft-bristled toothbrush.
- Avoid flossing the affected area.
- Use OTC painkillers.
Causes of Gum Abscess
Gum abscess occurs as a result of bacterial infection. However, each type occurs for a different reason.
Gingival Abscess Causes
A gingival abscess occurs when a foreign body such as toothbrush bristle or food is trapped in the space between the tooth and the gum near the coronal part of the gingiva (gingival margin). It doesn’t affect the tooth or the tissue that support the tooth (the periodontal ligament).
Periodontal Abscess Causes
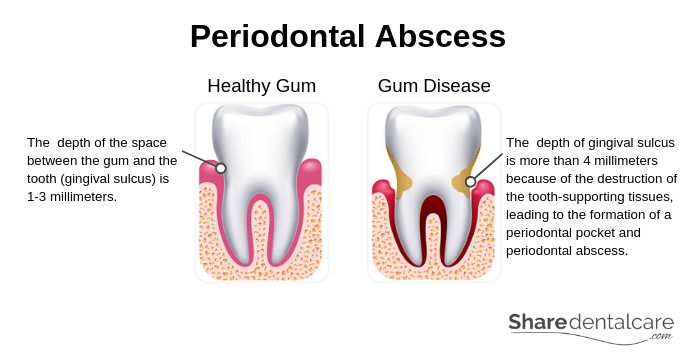
In healthy gums, the depth of the space between the gum and the tooth is 1-3 millimeters. This space is known as the gingival sulcus. With gum disease, the gum becomes inflamed and the gingival sulcus becomes more than 4 millimeters in depth because of the destruction of the tissues that support the tooth (alveolar bone and periodontal ligament), causing the formation of a periodontal pocket. This pocket is very hard to clean and can become an infected space easily, leading to the formation of a periodontal abscess.
Pericoronal Abscess Causes
A pericoronal abscess occurs as a result of pericoronitis, an inflammation of the gum tissue covering a partially erupted or impacted tooth. It is usually associated with partially erupted or impacted lower third molars (wisdom teeth).
Combined Endo-Perio Lesion
The combined endo-perio lesion occurs when the bacterial infection originated from the tooth spreads to the surrounding tissues. When bacteria enter the pulp through dental caries or crack in the tooth, it will lead to the formation of periapical abscess at the root tip. This abscess may spread to the gum through the periodontal ligament.
Risk Factors
Gum abscess occurs as a result of bacterial infection. There are several factors that may increase the risk of a gum abscess, include:
- Poor oral hygiene: if you don’t brush and floss your teeth regularly, this can lead to plaque buildup and increases the risk of gum disease and gum abscess.
- Smoking: tobacco smoking increases the risk of periodontal disease and periodontal abscess.
- Teeth clenching: grinding or clenching your teeth puts excessive pressure on the tooth-supporting tissues, leading to the destruction of the periodontal ligament.
- Consumption of sugary foods and drinks: poor oral hygiene, excessive consumption of sugary foods and drinks, and broken tooth fillings increase the risk of dental caries. Untreated dental caries can spread to the dental pulp, leading to the formation of periapical abscess which can spread to the surrounding tissues.
- Poor nutrition: a diet low in important nutrients can worsen the condition of your gum. Also, it compromises your body’s immune system which makes it harder for your body to fight infection.
- Medications: some medications such as hypertension medication and antidepressants can affect your gums.
- Medical conditions: some medical conditions such as diabetes mellitus, cardiovascular disease, and rheumatoid arthritis may worsen the condition of the gum.
Diagnosis of Gum Abscess
If you have persistent pain, bad taste in your mouth, or swollen gum, visit your dentist as soon as possible and don’t ignore these signs and symptoms. Your dentist will examine the affected area and take an x-ray.
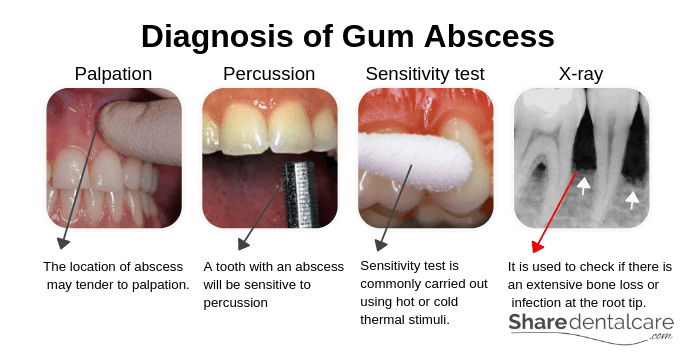
- Palpation test: your dentist will use one hand to identify the location of abscess which may tender to palpation.
- Percussion test: your dentist will use an instrument such as a mirror handle to tap on teeth to identify the affected tooth. A tooth with a periapical abscess will be sensitive to vertical percussion (with the long axis of the tooth). A tooth with a periodontal abscess will be more sensitive to horizontal percussion (perpendicular to the long axis of the tooth).
- Sensitivity test: this test is performed to determine whether the tooth is vital or not. The periapical abscess is usually associated with a non-vital tooth while the periodontal abscess is usually associated with a vital tooth.
- X-ray: your dentist will use X-ray to check for periodontal disease (periodontitis) or infection at the root tip (periapical abscess).
- CT scan: if the infection has spread to other parts of the body, your dentist may order a CT scan.
Treatment of Gum Abscess
Visit your dentist as soon as possible because gum abscess won’t heal on its own and untreated abscess can spread to other parts of the body such as the neck, causing serious, even life-threatening complications. Treatment of gum abscess include:
- Abscess drainage: your dentist may make a small cut (incision) in the gum to drain a large gum abscess. Then, he/she will use saline (salt water) to clean the area. This is a temporary solution to speed the healing process, relieve the pain, and prevent complications, and further treatment will be needed.
- Scaling and root planing: your dentist may perform scaling and root planing to remove tartar and bacteria from teeth surfaces, clean the periodontal pockets, and speed the healing or reattachment of the gum to the tooth surfaces.
- Surgical treatment: in the case of advanced gum disease (advanced periodontitis), the treatment may include surgical procedures such as pocket reduction surgery, soft tissue grafts, and bone grafting.
- Root canal treatment: if the gum abscess occurs due to the spread of infection from the tooth to the surrounding tissues (combined Endo-Perio lesion), your dentist may perform a root canal treatment (RCT). It involves the removal of dead pulp tissues and cleaning of the root canals with dental files and disinfectant solution to eliminate the infection. Also, your dentist may perform a root canal treatment if the infection has spread from a periodontal pocket to the dental pulp through accessory canals (combined Perio-Endo lesion), leading to the death of pulp tissues.
- Tooth Extraction: if the tooth is severely damaged, or there is an extensive bone loss in the bone that supports the tooth and tooth mobility, your dentist may extract the affected tooth.
- Operculectomy: in the case of a pericoronal abscess, your dentist may recommend the removal of gum tissues that covers the impacted or partially erupted tooth.
- Extraction of wisdom tooth: also, the treatment of pericoronal abscess may include the extraction of impacted or partially erupted lower wisdom tooth to prevent further occurrence of the abscess.
Gum Abscess Antibiotics
If the gum abscess is severe, your dentist may prescribe a course of antibiotics to help bring the infection under control and prevent the spread of infection to other areas such as the ear, jaw, and neck. However, antibiotics can’t replace the treatment.
When to See a Dentist?
If you have persistent pain or gum swelling, visit your dentist as soon as possible. He/She will relieve the pain and eliminate the infection to prevent the spread of infection to other parts of the body. Go to the emergency room (ER) if the gum abscess is associated with fever, or swelling of the neck. This means that the infection has spread to other areas and require immediate medical attention. Other signs and symptoms of a serious infection include:
- Severe facial swelling.
- Limited mouth opening.
- Difficulty breathing or swallowing.
- Swelling of the neck.
- Tenderness of the lymph nodes in the neck.
- High fever (more than 38°C)
Complications of Gum Abscess
An untreated abscess can spread to other areas, causing complications such as:
- Periapical abscess: if the periodontal abscess is left untreated, the infection may spread to the pulp of the neighboring tooth through accessory canals, leading to the death of pulp tissues and formation of periapical abscess at the root tip (Combined Perio-Endo lesion).
- Maxillary sinusitis: if the infection has spread to the maxillary sinuses, it may cause pain, headache, nasal discharge, and fever.
- Ludwig’s angina: if the infection has spread to the floor of the mouth, it may cause swelling around the mandible and upper neck, elevation of the floor of the mouth, and difficulty breathing and swallowing. This condition is known as Ludwig’s angina and it is a life-threatening condition.
- Osteomyelitis: if the infection has spread to the bone through the bloodstream, it may cause severe pain in the affected bone, fever, and nausea. This condition is known as osteomyelitis and it usually affects the bone near the site of gum abscess. However, the infection can spread to any bone in the body through the bloodstream.
- Sepsis: it is a potentially life-threatening condition that occurs due to dysregulated body’s response to an infection.
Prevention of Gum Abscess
To prevent gum abscess, you should:
- Maintain good oral hygiene: brush your teeth with a soft-bristled toothbrush at least twice a day, especially before sleep. Also, clean between your teeth with dental floss at least once a day.
- Eat a healthy diet: eat a diet that contains a variety of foods to keep your gums healthy, and limit sugary and acidic foods and drinks.
- Visit your dentist regularly: schedule an appointment with your dentist at least once every six months for professional cleaning. Also, your dentist can diagnose and treat oral problems early to prevent complications.
Conclusion
Do you have persistent pain or gum swelling? Do you suspect that you have a gum abscess? Visit your dentist as soon as possible to relieve the pain and eliminate the infection. Untreated gum abscess may spread to other parts of the body such as the neck, causing serious, even life-threatening complications. Use OTC painkillers to relieve the pain until you are able to see your dentist. Also, don’t bite or chew on the affected area.