The dental bridge is a fixed dental prosthesis that is supported by teeth or dental implants and replaces a missing tooth or teeth. Tooth loss causes the formation of gaps in the dentition that can affect chewing function, speech, and aesthetic appearance. A dental bridge is needed to close these gaps and replace the missing tooth or teeth. If the gap exists over a long period of time, this will cause the movement of neighboring teeth in the direction of the gap and the overeruption of opposing teeth. In this case, the replacement of the missing tooth or teeth will be difficult and a complex procedure will be needed to create an adequate space for the bridge.
What is a Dental Bridge?
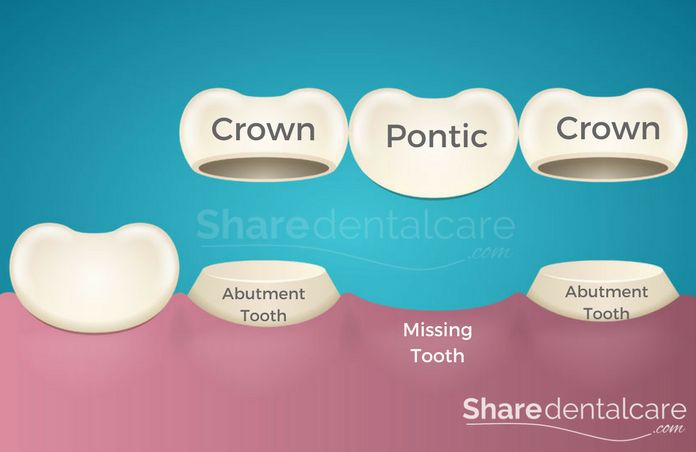
The dental bridge is a fixed dental prosthesis. It consists of two or more crowns that are attached to natural teeth (abutment teeth) and holding a false tooth or teeth (pontic) in between. The bridge can be supported by natural teeth or dental implants.
Types of Dental Bridge
Traditional Dental Bridge
It is the most common type. It consists of one or more false teeth (pontics) that are held in place by dental crowns. These crowns are attached to natural teeth (abutment teeth) on both sides of the gap. Also, it can be supported by dental implants. This type can withstand chewing force. So, it can be used in the posterior area (molar teeth).
Cantilever Bridge
This type is not very common. The pontic is attached to the dental crown (abutment tooth or teeth) at only one side of the gap rather than both sides like the traditional bridge. This type is not recommended in the posterior area (molar teeth), because the chewing force (leverage force) can cause damage to the abutment tooth or loosen the crown.
Maryland Bridge
It is also known as a resin-bonded bridge. Maryland Bridge doesn’t use dental crowns for support. The pontic (false tooth) is held in place by wings bonded to the back of the neighboring teeth. This type is considered more conservative than the traditional bridge because minimal or no tooth preparation is required. However, it tends to debond especially in areas subjected to a lot of chewing force.
Dental Bridge Materials
The materials used in the manufacture of the bridge are the same as the material used in the manufacture of the dental crown.
Gold and Metal Alloys
Gold and metal are characterized by stability and long durability. However, they are unaesthetic therefore, they are mainly used in non-visible areas (molar teeth).
All-Ceramic
It has a great aesthetic appeal. However, ceramics are not resistant to breakage as metal therefore, they are made thicker, and more tooth-hard substances are removed to make a room for the bridge.
Porcelain-Fused-to-Metal
It is a combination of porcelain and metal. The porcelain mimics the color of natural teeth and the metal provides strength and stability.
Dental Bridge Procedure: How It Works?
Dental bridge procedure requires multiple visits to the dental office, depending on the complexity of the bridge. Usually, three visits are sufficient.
The First Appointment
During the first appointment, the dentist examines the surrounding teeth and takes a few X-rays. Any caries that may be present must be removed and a tooth filling should be placed as well. The tooth color is determined during the first appointment. Then, the dentist prepares the abutment teeth, and hard tooth substances (tooth enamel) are removed to make a room for the bridge. Abutment teeth must be parallel to each other. After the preparation, the dentist takes an impression and sends it to the dental lab. A temporary bridge is placed to protect the prepared teeth.
The Second Appointment
During the second appointment, the dental lab sends the bridge framework, called a try-in. The dentist checks the accuracy, fitting, and comfortableness of the bridge. Then, they send the try-in back to the dental lab to complete the processing of the bridge.
The Third Appointment
During the third appointment, the temporary bridge is removed and the permanent bridge is cemented in place with temporary cement to make sure it fits properly. After one or two weeks, the permanent bridge is cemented permanently in place.