Dental implants are artificial tooth roots that are firmly anchored in the jawbone. They provide support for dental prostheses (crowns, bridges, and dentures) to replace a missing tooth or teeth. With few exceptions, implants are suitable for almost all patients. They are made of titanium or zirconia that are compatible with the human body. After the placement of implants in the jawbone, they fuse with the surrounding bone tissue. This process is known as osseointegration which involves a direct connection between dental implants and living bone tissues. In most patients, osseointegration occurs without complications.
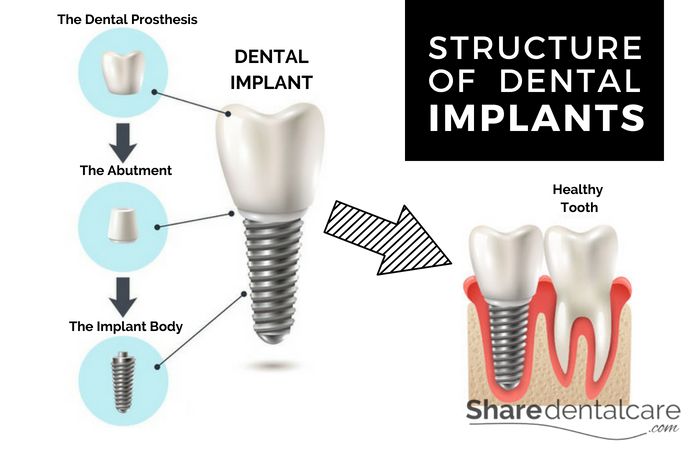
Structure of Dental Implants
The Implant Body
The implant body performs the same function as the original tooth roots. The dentist or oral surgeon inserts the implant body in the jawbone (below the gum line). Then, it fuses with the surrounding bone tissue (osseointegration). The implant body is made of titanium or zirconia.
The Abutment
The abutment is the neck part. It connects the implant body with the dental prosthesis (crown, bridges, and dentures). The dentist attaches the abutment to the implant body after the healing period (4 to 6 months).
The Dental Prosthesis
The dental prosthesis can be fixed (crowns or bridges) or removable (dentures). The selection of the dental prosthesis depends on the number of missing teeth, the quality of the bone, the patient’s desire, and other factors. You can read more about bridge types in dentistry.
Dental Implants Material
Dental implants are made of titanium or zirconia. Both materials are compatible with the human body, FDA-approved, and considered safe. Titanium implants are widely used because they have some advantages over zirconia implants such as ease of placement and resist fracture in places with high chewing load. However, zirconia implants have a very similar color to natural teeth and can be used in places with aesthetic problems.
What are The Pros and Cons of Dental Implants?
Pros
The big advantage of implants over conventional prostheses is the replacement of missing teeth without the need to prepare the adjacent teeth for support. Also, they have a very long shelf life, are resistant to high chewing force, can be cleaned easily, and can be used in the case of loss of several teeth or all teeth.
Cons
Dental implant surgery involves certain risks that may arise during the procedure (including injuries to adjacent teeth, nerve damage, and bleeding) and after the procedure (including prolonged bleeding, delayed healing, and the failure of osseointegration.
Also, implants require daily oral hygiene and regular visits to the dentist for prophylactic examinations. If daily oral hygiene is not sufficient, this can lead to a destructive inflammatory process affecting the gum and bone that surrounds the dental implants (peri-implantitis), leading to failure. Compared to bridges and dentures, implants are more expensive.
Are Dental Implants For Everyone?
With few exceptions, dental implants are suitable for almost all patients. Anyone healthy enough to undergo oral surgery and have healthy bone and gum can be considered for dental implants. Diabetes mellitus and smoking are generally considered to be risk factors, but this won’t prevent the implantation. Each case needs to be evaluated on an individual basis.
Contraindications
Typical contraindications include:
- Children and adolescents.
- During pregnancy.
- Metabolic disorders (eg: poorly controlled diabetes mellitus).
- Diseases of the kidney, liver, and bone.
- Heavy smoking.
- Alcohol, and drug abuse.
- The nerves are too close to the implant.
- An insufficient bone thickness and the maxillary sinus is too close.
- Acute infectious diseases.
- Immunological diseases.
- Recent radiotherapy.
- Active cancer.
- Osteoporosis (bone loss).
- Bruxism.
Dental Implants Procedure
Preoperative
First, the dentist will ask about your previous or existing medical conditions. Then, they will examine your oral cavity and ask for an x-ray and cone beam computed tomography (cone beam CT) to plan the exact position of dental implants. Also, the dentist will treat existing dental problems such as gum disease.
Dental Implants Procedure
In most cases, the dentist performs the dental implant procedure under local anesthesia. After the injection of a local anesthetic, the dentist makes an incision in the gum and drills in the jawbone. Then, they insert the titanium or ceramic implants into the bone and close the gum over the dental implants with a few stitches.
Sufficient bone thickness is important for the success of the implantation. If there is not enough bone thickness, the dentist or oral surgeon will perform a procedure known as bone augmentation or bone graft to rebuild the bone and support dental implants.
Healing
During the healing period, the dental implant fuses with the surrounding bone tissues (osseointegration). The healing period depends on the quality of the bone. In the upper jaw, it takes 3 to 6 months. In the lower jaw, it takes 2 to 4 months.
The Prosthesis
Once the healing process is complete, the dentist will attach the abutment to the implant body. Then, they will take an impression and send it to the dental lab for the production of the dental prosthesis (crowns, bridges, and dentures).
What are The Risks of the Implant Procedure?
Despite the risks involved, dental implants are the best choice to replace a missing tooth or teeth and have many advantages compared to conventional prostheses. Patients interested in implants should be aware of the risks:
- Allergy-related to titanium implants.
- Nerve injury.
- Injury to blood vessels.
- Injury to adjacent teeth.
- Delayed healing after the procedure.
- Swelling.
- Bleeding.
- Bruising.
- Pain.
- Peri-Implantitis.
- Loss of dental implants.