Gum disease is a common oral problem in humans. Most people don’t realize that they have gum disease until the condition has advanced to a very serious stage. Gum disease can lead to tooth loss if not treated properly. Also, it is linked to other diseases such as pneumonia and even heart attack. In this blog post, we’ll discuss what causes gum disease in humans and what the symptoms are.
What’s Gum Disease?
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a bacterial gum infection that can damage the gums and tissues that support teeth. It’s a common oral disease that can lead to tooth loss if left untreated. Stages of gum disease include:
- Gingivitis: It is the mild and early stage of gum disease. Gingivitis is a reversible condition.
- Periodontitis: It is the advanced stage of gum disease. Periodontitis takes longer to develop than gingivitis, but once it develops, it progresses more rapidly and leads to greater destruction of the supporting tissues.
How Does Gum Disease Occur in Humans?
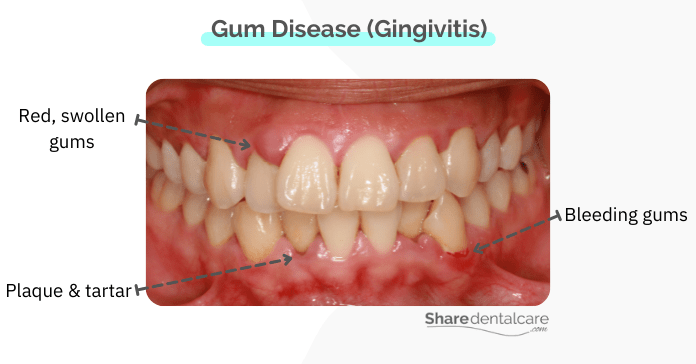
Humans’ mouths contain different types of bacteria, some of these bacteria are harmful and may contribute to gum disease. Dental plaque is a sticky, colorless film of bacteria. It builds upon your teeth and gums every day. Plaque bacteria break down food (carbohydrates) and produce acids that irritate the gums, causing inflammation of the gums. Find out what bacteria cause gingivitis. The gums also become red and swollen. This stage of gum disease is known as gingivitis, which can be easily treated by good oral hygiene practices and professional teeth cleaning. Gingivitis is a reversible condition.
However, if care is not taken, the bacterial infection may spread to deeper tissues in the mouth. This stage is known as periodontitis, which causes damage to the tooth-supporting tissues and can lead to tooth loss. Gum disease is difficult to cure once it’s at this stage.
Causes & Risk Factors for Humans Gum disease
Several factors make dental plaque accumulation easier, allow bacterial growth, and increase the risk of gum disease. The risk factors and causes of gum infection include:
- Poor oral hygiene: If you don’t brush or floss your teeth regularly, dental plaque will accumulate on your teeth and gums.
- Smoking and tobacco use: They weaken the humans’ immune system, making it harder for your gums to fight gum disease. Smoking is one of the common causes of gum disease.
- Dental problems: Crooked teeth, misaligned teeth, cavities between molars, and broken tooth fillings.
- Dental appliances: They allow plaque to accumulate. For example, poorly fitted dentures and bridges, and orthodontic appliances.
- Hormonal changes: During pregnancy, puberty, and menstrual cycle. Find out more about pregnancy gingivitis.
- Dry mouth condition, which allows bacteria to grow in the mouth, causing gum disease.
- Some medications cause inflammation of the gums as a side effect, for example, oral contraceptives, steroids, anticonvulsants, calcium-channel-blockers, and chemotherapy drugs.
- Certain medical conditions: Gum disease may occur as a manifestation of some systemic diseases such as human immunodeficiency virus, cancer, and diabetes.
Signs & Symptoms of Gum Disease in Humans
Most people are not aware that they have gum disease because it may progress painlessly, making few obvious signs, even in the advanced stage. Recognizing the early signs of gingivitis can help prevent gum disease and keep a healthy mouth. Here are the signs and symptoms of gingivitis and periodontitis:
Gingivitis – The Early Stage
- Red, puffy gums
- Gums are tender to touch
- Gum bleeding when brushing or flossing
- Persistent bad breath
- Mild gum recession
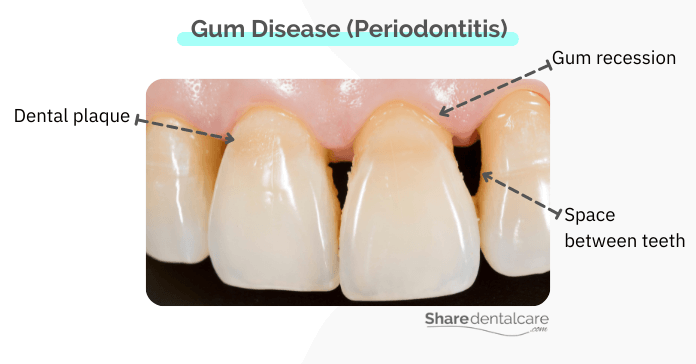
Periodontitis – The Advanced Stage
- Severe gum recession
- Periodontal pockets
- Developments of spaces between teeth
- Gum abscess
- Changes in the way teeth fit together (malocclusion)
- Tooth mobility
- Tooth loss
Treatment of Gum Disease in Humans
The treatment of gum disease depends on its severity. Gingivitis is a reversible condition, which can be treated by improving your oral hygiene at home and professional teeth cleaning at the dental office. Improving your oral hygiene includes:
- Brush twice a day with a soft-bristled toothbrush.
- Flossing your teeth daily.
- Use an antimicrobial mouth rinse.
- Stop smoking. If you can’t quit smoking, at least avoid it as much as possible.
- Eat a nutrient-rich diet that is low in carbohydrates.
- Limit sugary foods and drinks.
In the case of periodontitis, your dentist may recommend a more advanced treatment plan, which includes:
- Scaling and root planing.
- Flap surgery for deep scaling and root planing.
- Soft tissue graft for gum recession.
- Bone grafting to replace the lost bone support.
Gum Disease in Humans – Conclusion
Gum disease is a bacterial infection that can damage the gums and tissues that support human teeth. Gum disease can lead to tooth loss if not treated in time. Gingivitis is the early stage of gum disease, which causes red, swollen gums that bleed easily. Gingivitis can be reversed by improving oral hygiene and professional teeth cleaning. If left untreated, gingivitis progresses to periodontitis, which can cause bone loss, tooth mobility, and tooth loss. Gum disease is difficult to cure once it’s reached the advanced stage. So, it’s important for you to recognize the signs and symptoms early to prevent complications. Also, visit your dentist regularly for professional teeth cleaning.