An operculum is a flap of gum tissue that covers the crown of a partially erupted tooth. It usually affects the lower third molars, especially when they don’t have enough room to erupt through the gums. The operculum can become inflamed and painful, making it difficult to open your mouth or chew. In this blog post, we’ll discuss what you can do to treat an inflamed operculum and get relief from the pain.
What is Pericoronitis and What Causes It?
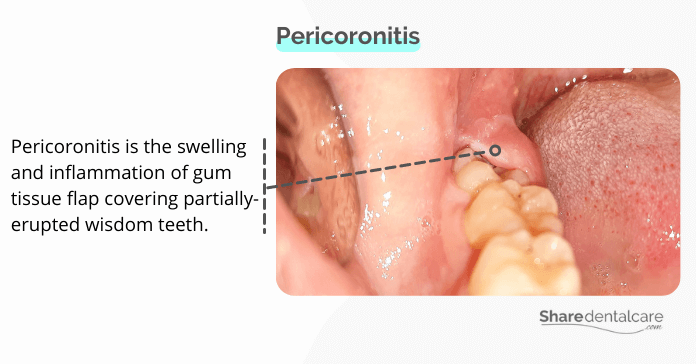
Pericoronitis is a condition in which the operculum, a gum tissue flap covering a partially erupted tooth, becomes inflamed, swollen, and painful. This can happen when food and bacteria become trapped under the operculum, causing an infection.
Pericoronitis is most common in the lower third molars, also known as wisdom teeth because they are the last teeth to erupt and often don’t have enough room to do so. The operculum covering a wisdom tooth can become inflamed, swollen, and red. It can also make it difficult to open your mouth or chew. Pericoronitis can occur without wisdom teeth in fewer cases.
Risk Factors
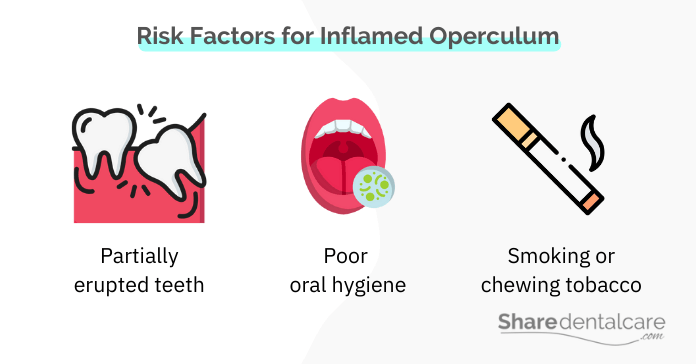
Several factors can increase your risk of developing pericoronitis, including:
- Partially erupted teeth: If your wisdom teeth are only partially erupted, the operculum covering them is more likely to become inflamed.
- Poor oral hygiene: If you don’t brush and floss regularly, bacteria can build up in your mouth and lead to an infection.
- Crooked teeth: If your teeth are crooked, they may be more difficult to clean and more likely to trap food and bacteria.
- Hormonal changes: Hormonal changes, such as those that occur during puberty or pregnancy, can make the gums more susceptible to inflammation.
- Smoking: Smoking can increase your risk of developing pericoronitis because it decreases the production of saliva, which helps to keep the mouth clean. You can read more about how smoking can cause periodontal disease.
Symptoms Associated with Inflamed Operculum
The most common symptom of pericoronitis is pain. The operculum can become infected and swollen, making it difficult to open your mouth or chew. Other symptoms include:
- Redness and swelling of the operculum
- Tenderness and pain when chewing
- Bad taste in the mouth
- Pus discharge (pocket of pus in gums)
- Bad breath. You can read more about pericoronitis smell.
- Trismus (lockjaw)
If you experience any of these symptoms, see your dentist as soon as possible.
Home Remedies for Inflamed Operculum
Several home remedies can help to reduce the pain associated with an infected operculum. These include:
- Over-the-counter pain relievers: Ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help to reduce pain and inflammation.
- Salt water mouth rinses: Mix 1/2 teaspoon of salt in a cup of warm water and use it to rinse your mouth 3-4 times a day.
- Brushing and flossing: Brush your teeth twice a day and floss daily to remove food and bacteria from your teeth.
- Avoid hard and chewy foods: Avoid hard and chewy foods that can irritate the inflamed operculum.
Home remedies don’t cure inflamed operculum. However, they may help to reduce pain and inflammation. Home remedies don’t replace the need for professional medical treatment. If you have a painful operculum, see your dentist as soon as possible. You can read more about the pericoronitis home remedy.
Complications of Inflamed Operculum
If the infected operculum is left untreated, the condition may worsen, and the infection may spread to other parts of the mouth, causing severe pain, lockjaw (trismus), difficulty swallowing, and fever.
In rare cases, the infection can spread to the head and neck, causing Ludwig’s angina, a life-threatening condition. Also, in rare cases, the infection can spread to the bloodstream and cause sepsis, which is also a life-threatening condition.
Treatment for Inflamed Operculum
The goal is to reduce inflammation and pain and to prevent the infection from spreading. Treatment options include:
- Pain relief: Pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can help to reduce the pain associated with an inflamed operculum.
- Antibiotics: Your dentist may prescribe antibiotics to help control the infection.
- Surgical treatment: your dentist may remove the inflamed operculum or the tooth.
- Operculectomy: If the wisdom tooth erupts normally, your dentist may recommend the removal of the operculum. Operculectomy is a surgical procedure to remove the infected operculum.
- Tooth extraction: if the wisdom tooth is impacted or damaged, your dentist may recommend that it be removed.
After the treatment of an inflamed operculum, it’s important to practice good oral hygiene to prevent the infection from recurring. This includes brushing twice a day, flossing daily, and using an antibacterial mouthwash.
Conclusion
An inflamed operculum is a condition that can be painful and uncomfortable. If you have an inflamed operculum, see your dentist as soon as possible to prevent this condition from worsening. Several treatment options are available, including pain relief, antibiotics, and surgery.
After the treatment, it’s important to practice good oral hygiene to prevent the infection from recurring. This includes brushing twice a day, flossing daily, and using an antibacterial mouthwash.