A congenitally missing tooth is when the tooth never develops in the mouth. This condition is known as hypodontia, which can affect primary or permanent teeth. Hypodontia is very rare in primary dentition, but it can affect the upper lateral incisors. In most cases, when a lateral incisor in baby teeth is missing, the permanent lateral incisor is also found to be missing.
What is Hypodontia?
Congenitally missing teeth is a condition known as hypodontia, which refers to the developmental failure/absence of six or fewer teeth. This means that the person has fewer teeth than normal. Hypodontia is common in adults, which affects from 1.6 to 6.9% of the population. However, it is a rare condition in the primary teeth. The developmental failure of teeth can be divided into:
- Hypodontia: the absence of 6 or fewer teeth.
- Oligodontia: the absence of more than 6 teeth.
- Anodontia: the complete absence of teeth.
Is My Child’s Baby Teeth Lateral Incisor Congenitally Missing?
The lateral incisor in baby teeth usually erupts by the age of 9-13 months old. The parents should check if it is missing by this time. It is rare but possible to have a congenitally missing baby teeth lateral incisor in some cases.
If your child’s primary lateral incisor didn’t erupt by the age of 13 months, visit your dentist to have it examined. You may need an X-ray to see the whole jaw. In some cases, the missing tooth is due to a delay in tooth eruption.
The American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry recommends that you visit your primary care provider any time you suspect there is a problem with your baby’s teeth or mouth. They can help identify issues early so that treatment can begin sooner.
Causes of Congenitally Missing Baby Teeth Lateral Incisor
The lateral incisor usually erupts between 6 and 13 months of age. The exact cause of the missing lateral Incisor is still unclear. However, several studies suggest that it occurs due to genetic, environmental factors, or a combination of both.
- Genetic factors: a single gene defect may contribute to hypodontia. Children with Down syndrome or siblings of children with a cleft lip and/or palate were more likely to have congenitally missing baby teeth lateral incisor than those without these conditions.
- Environmental factors: trauma, infectious diseases, and systemic problems such as rickets can disrupt the initial stages of tooth development.
- Heredity may also be a factor due to patterned missing teeth in your family history.
Treatment of Missing Lateral Incisor in Baby & Permanent Teeth
The treatment of missing baby teeth lateral incisor is not necessary. If the existing teeth are in good condition and there are no other issues such as crowding in the jaw or soft tissue problems, then this missing tooth may have no effect on your child’s oral health. However, when your child grows up, they may need dental treatment because when a lateral incisor in baby teeth is missing, the permanent lateral incisor is also found to be missing. In the case of congenitally missing permanent teeth, the treatment options include correcting it by orthodontic treatment or getting a fake tooth.
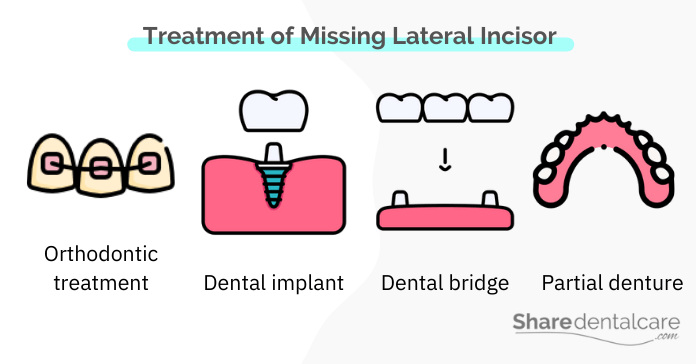
- Orthodontic treatment: your orthodontist can close the space with orthodontic treatment or widen the space of the missing permanent tooth for implant placement.
- Dental Implant: it is the best option to replace a permanent missing lateral incisor because implants are strong, durable, and aesthetic.
- Dental bridge: it is a fixed prosthesis that is supported by the adjacent teeth. Bridges are less invasive than implants, but they cause damage to the adjacent teeth. Learn more about bridge types in dentistry.
- Partial denture: it is a removable prosthesis that is less expensive than bridges and implants. However, this is not a long-term solution. Learn more about the pros & cons of a denture for 1 tooth.
The dentist will assess the overall health of your child’s mouth before deciding what treatment will be provided. Read more about fake teeth for missing teeth.
Conclusion
Hypodontia occurs when a tooth fails to develop in the mouth. This can be due to genetic, environmental factors, or a combination of both. Missing baby teeth lateral incisors is a rare condition. However, if your child’s lateral incisors are missing, visit your dentist to check whether the eruption is delayed or the child’s teeth failed to develop.
Missing lateral incisors in primary teeth don’t require treatment. However, when a lateral incisor in baby teeth is missing, the permanent lateral incisor is also found to be missing. So, if permanent lateral incisors are missing, your child may need orthodontic treatment, implants, or bridges when they get older.