Do you have pockets between your teeth and gums? Pockets form when the gum tissue pulls away from the tooth, creating a space where bacteria can thrive. They can accumulate food and bacteria, leading to discomfort or pain. If pockets are left untreated, they can lead to tooth loss. In this blog post, we will discuss what pockets are, how they form, and how they can be treated.
What are Pockets between Teeth and Gums?
Periodontal pockets, also known as gum pockets, are spaces or openings that form around the teeth under the gum line. They can become filled with infection-causing bacteria. Pockets occur as a result of periodontitis, an advanced form of gum disease. If left untreated, pockets will become larger and deeper, eventually causing the gum tissue and bone to break down. This can lead to tooth loss.
The Severity of Pockets between Teeth and Gums
Pockets are classified according to their depth.
- A shallow pocket is one that is less than three millimeters deep.
- A moderate pocket is three to six millimeters deep.
- A deep pocket is more than six millimeters deep.
The depth of a pocket is determined by measuring the distance from the top of the gum tissue to the bottom of the pocket. The deeper the pocket, the more severe the periodontitis and the greater the risk of tooth loss.
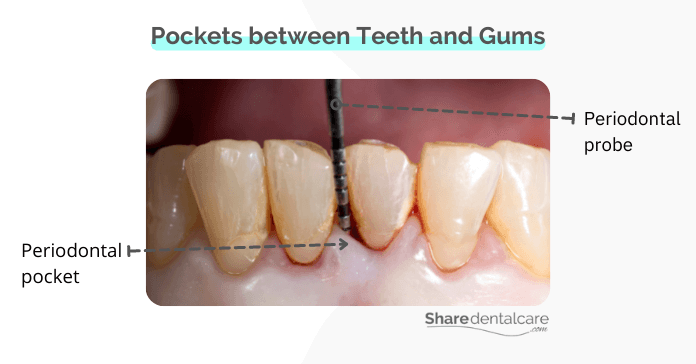
How Do Pockets Develop between Teeth and Gums?
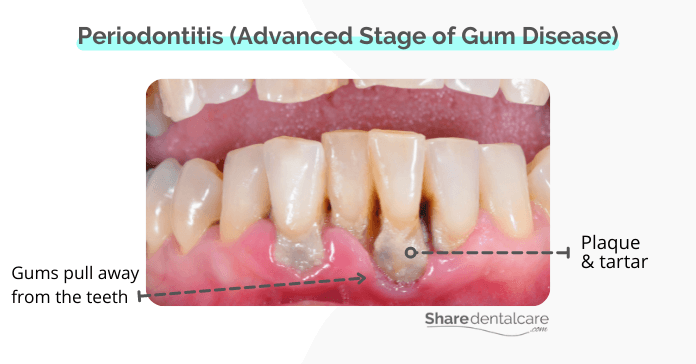
Pockets between teeth and gums are a symptom of periodontitis. Periodontitis is an advanced form of gum disease that occurs due to the buildup of plaque and tartar on teeth surfaces. Dental plaque is a sticky film of bacteria that forms on the teeth.
If plaque is not removed regularly, it can harden and turn into tartar. Tartar can irritate the gums and cause them to become inflamed. The inflammation can cause the gum tissue to pull away from the teeth, creating pockets.
The following symptoms may be associated with pockets between teeth and gums:
- Swollen or puffy gums
- Red gums that bleed easily
- A pocket of pus in the gums
- Bad breath
- The development of spaces between your teeth
- Gums pull away from your teeth (gum recession)
- Loose teeth or tooth loss
Risk Factors for Pockets between Teeth and Gums
There are several factors that can increase your risk of developing pockets between teeth and gums. These include:
- Poor oral hygiene.
- Smoking and tobacco use.
- Dry mouth condition.
- Crooked teeth.
- Vitamin C deficiency.
- Hormonal changes during pregnancy (pregnancy gingivitis) or menopause.
- Diabetes.
- Certain medications can cause dry mouth as a side effect.
- Diabetes and other medical conditions can lower the body’s ability to fight infection.
If you have any of these risk factors, it is important to see a dentist or periodontist regularly for checkups and professional teeth cleaning.
Diagnosis
Pockets are usually diagnosed during a regular dental checkup. Your dentist or periodontist will examine your mouth and look for signs of gum disease, such as pockets, gums that are red or swollen, and bleeding gums. They will also measure the depth of any pockets that are present. X-rays may also be taken to assess the severity of the gum disease.
If pockets are found, your dentist or periodontist will develop a treatment plan to reduce the pockets and improve your oral health.
How Pockets between Teeth and Gums are Treated?
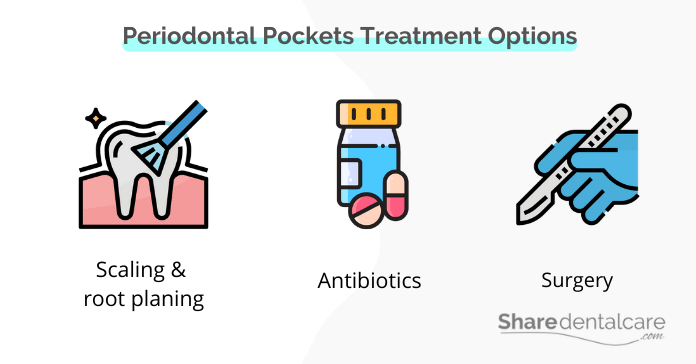
Treatment for pockets between teeth and gums will vary depending on the severity of the condition. The goal of treatment is to reduce the pockets and improve oral health. Treatment options include:
- Scaling and root planing: it is a non-surgical procedure that involves removing plaque and tartar from the teeth and smoothing the roots of the teeth. This helps to remove bacteria and reduce pockets between teeth and gums.
- Antibiotics: Your dentist may prescribe antibiotics to help control the infection.
- Surgery: In deep pockets, surgery may be necessary to treat the pockets and remove the infected tissue, for example:
- Pocket Reduction Surgery: It involves lifting the gum tissue and exposing the tooth’s root. Then, the dentist will perform deep scaling and root planing. The gum tissue is then repositioned and stitched into place.
- Bone Grafting: It may be necessary to replace bone that has been lost due to periodontitis.
- Gum grafting: It may be necessary to replace gum tissue that has been lost due to periodontitis.
It is important to see a dentist or periodontist regularly for checkups and professional teeth cleaning even after treatment has been completed. This can help to prevent pockets from returning.
You can read more about loose teeth after deep cleaning.
Prevention
Good oral hygiene is essential to prevent pockets between teeth and gums.
- Brush your teeth at least twice a day. Use a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste.
- Floss your teeth at least once a day. Toothbrushes can’t reach and clean spaces between teeth. Use dental floss to remove plaque between teeth.
- Use an antibacterial mouthwash. Antibacterial mouthwash helps wash away food debris and reduce plaque build-up.
- Quit smoking. Smoking is a major risk factor for gum disease (periodontitis), pockets between teeth and gums, and oral cancer. You can read more about smokers gums treatment.
- Visit your dentist regularly. Routine check-ups and professional teeth cleaning are essential for good oral health. Professional teeth cleaning can remove plaque and tartar from the teeth and prevent pockets from forming.
If you have any of the risk factors for pockets between teeth and gums, it is important to see a dentist or periodontist regularly for checkups. They can help to diagnose the condition early and develop a treatment plan to improve your oral health.
Conclusion
Pockets between teeth and gums are a symptom of periodontitis, an advanced stage of gum disease. Several factors can increase your risk for pockets, including smoking, poor oral hygiene, and certain medical conditions. Treatment for pockets between teeth and gums will vary depending on the severity of the condition, for example, scaling and root planing or surgery.
Good oral hygiene is essential for preventing pockets between teeth and gums. Brush your teeth at least twice daily with fluoride toothpaste and floss daily. Also, visit your dentist or periodontist regularly for checkups and professional teeth cleaning.