A tooth abscess is a collection of pus that can form in different parts of the oral cavity as a result of bacterial infection. It can cause pain that increases in severity with pressure or heat. Also, tooth abscess may cause gum swelling, pus discharge, facial swelling, and tenderness of the lymph nodes. Visit your dentist as soon as possible if you have these signs and symptoms to get immediate tooth abscess treatment and relieve the pain. In this article, we will discuss:
- Types and causes of a tooth abscess.
- Can a tooth abscess go away on its own?
- When to see a dentist?
- What is the tooth abscess treatment options?
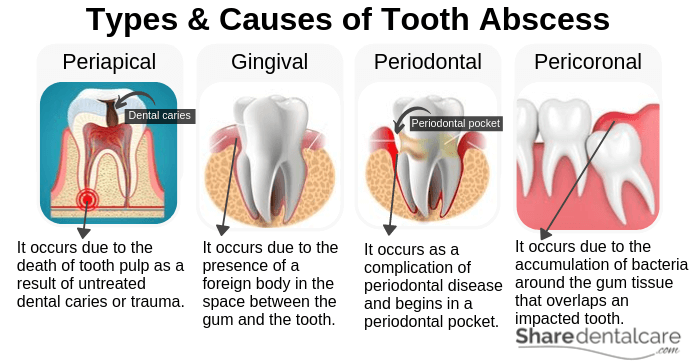
Types and Causes of Tooth Abscess
Tooth abscess treatment depends on the type of abscess. Each type occurs in a different place for a different reason and may require a different tooth abscess treatment.
- Periapical abscess: this type occurs due to the death of tooth pulp as a result of untreated dental caries or trauma. Periapical abscess forms around the root tip.
- Gingival abscess: This type occurs due to the presence of a foreign body in the space between the gum and the tooth. Gingival abscess doesn’t the tooth-supporting tissues (the periodontal ligament).
- Periodontal abscess: This type occurs as a complication of periodontal disease and begins in a periodontal pocket. Poor oral hygiene can lead to the inflammation of gum tissues and the formation of periodontal pockets (deep space around teeth). When these pockets become infected, this will lead to severe pain and formation of a periapical abscess alongside the tooth.
- Pericoronal abscess: This type occurs due to the accumulation of bacteria and food debris around the gum tissue that overlaps a partially erupted or impacted tooth. Pericoronal abscess is usually associated with partially erupted or impacted lower third molars (lower wisdom teeth).
Symptoms of Abscessed Tooth
A tooth abscess is usually painful. The pain occurs suddenly and gets worse over time. Other signs and symptoms include:
- Severe, persistent pain that can radiate to the jaw, neck, and ear.
- Sensitivity to hot or cold foods and drinks.
- Pain when biting or chewing.
- Gum redness and swelling.
- Loose teeth.
- Tooth discoloration.
- Bad breath.
- Facial redness and swelling.
Tooth Abscess Treatment: at Home
You can’t treat tooth abscess at home. However, you can try these home remedies to relieve the pain until you can see your dentist:
- Use over-the-counter painkillers to relieve the pain, for example, ibuprofen, paracetamol, or aspirin. Consult your doctor or pharmacist before taking OTC painkillers.
- Avoid hot or cold foods and drinks.
- Don’t chew on the affected side of your mouth.
- Eat soft, cool foods on the opposite side of your mouth.
- Don’t eat hard food.
- Use a soft-bristled toothbrush and don’t floss around the abscessed tooth.
- Sleep with your head elevated. Because the blood rushes to your head when you sleep, making the pain worse.
When to see your dentist?
Visit your dentist as soon as possible if you have persistent pain or gum swelling to get immediate tooth abscess treatment and prevent complications. An untreated abscess may spread to other areas, causing serious complications such as Ludwig’s angina and sepsis. Go to the emergency (ER) if you have the following and symptoms to get immediate medical attention:
- High fever and fatigue.
- Severe facial swelling.
- Swelling of the neck.
- Limited mouth opening.
- Difficulty swallowing and breathing.
So, you should visit your dentist as soon as possible to relieve the pain and get tooth abscess treatment before the infection spreads to other areas.
Tooth Abscess Treatment: at The Dental Office
The tooth abscess treatment depends on the underlying cause. So, your dentist will examine your oral cavity and use x-rays to determine the cause of the abscess. Then, your dentist will start the treatment. The goal of the tooth abscess treatment is to eliminate the infection and relieve the pain.
Drainage of the Abscess
In the case of a large abscess, your dentist will make a small cut in the gum to drain the pus. Then, your dentist will clean the area with saline. Drainage of the abscess is a temporary solution to relieve the pain and prevent the spread of infection to other areas. After that, you will need further treatment.
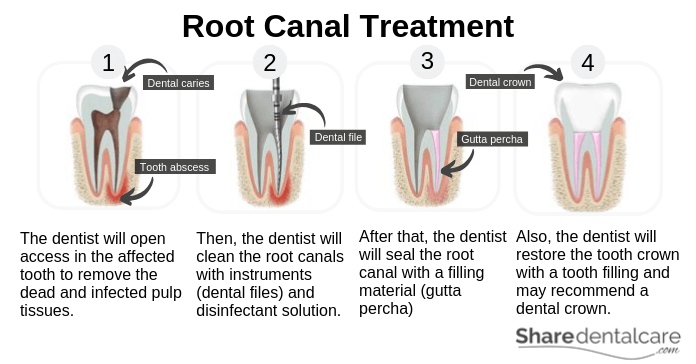
Root Canal Treatment
A root canal treatment is a procedure used to treat and save a tooth with inflamed and infected pulp tissues. The tooth pulp becomes infected and inflamed due to:
- Deep dental caries.
- Crack or chip in the tooth.
- Trauma.
- Large tooth fillings.
If the tooth pulp becomes inflamed and infected, this will lead to the death of the pulp tissues and the formation of an abscess around the root tip (periapical abscess). To treat the abscessed tooth, your dentist will perform a root canal treatment (RCT). first, your dentist will open access in the affected tooth to remove the dead and infected pulp tissues. Then, he/she will clean the root canals with instruments (dental files) and disinfectant solution to eliminate the infection. After that, your dentist will seal the root canal with a filling material (gutta percha) to prevent the recurrence of infection.
Also, your dentist will restore the tooth crown with a tooth filling such as composite or amalgam. Root canal treatment may require multiple visits to the dental office and its performed under local anesthesia. After RCT, your dentist will recommend a dental crown to protect the tooth and restore its function.
Scaling and Root Planing
Scaling and root planing is a procedure that involves the removal of plaque and calculus to help treat periodontal disease (advanced gum disease). Poor oral hygiene leads to plaque build-up, causing the inflammation of gum tissues (gingivitis). If the inflamed gum is left untreated, bacteria in plaque will produce toxins and poisons that break down the bone and connective tissue that hold teeth in place (periodontitis). This will lead to the formation of periodontal pockets which are small spaces between teeth and gums. These pockets collect food debris and can become infected, causing pain and the formation of a periodontal abscess. Several factors increase the risk of periodontal disease, include:
- Smoking.
- Poor nutrition.
- Poor oral hygiene.
- Changes in hormones.
- Medical conditions.
In this case, your dentist may recommend scaling and root planing for tooth abscess treatment. First, your dentist will remove plaque and calculus from your teeth and periodontal pockets (scaling). Then, your dentist will smooth the tooth roots (root planing) to help your gums to reattach to your teeth. Scaling and root planing may require multiple visits to the dental office. The tools used to perform the procedure include:
- Hand instruments (periodontal sealers and curettes).
- Ultrasonic devices.
- Laser devices.
After the procedure, your dentist may prescribe an antibiotic and a mouthwash to speed the healing process.
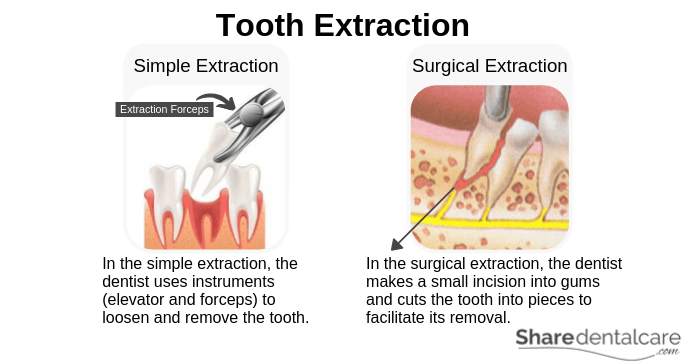
Tooth Extraction
Your dentist may recommend tooth extraction in the following cases:
- The tooth is severely damaged and can’t be restored.
- The infection is so severe that antibiotics and root canal treatment don’t cure it.
- The tooth is loose due to the destruction of the tooth-supporting tissues as a result of periodontal disease.
- Impacted or partially erupted tooth causing the formation of a periodontal abscess.
Tooth extraction is usually performed under local anesthesia by a dentist or oral surgeon. Tooth extraction can be simple or surgical. In the simple extraction, your dentist uses instruments (elevator and forceps) to loosen and remove the tooth. If the tooth is severely damaged, your dentist may perform a surgical extraction. your dentist will make a small incision into your gums and cut your tooth into pieces to facilitate its removal.
Tooth Abscess Treatment: Antibiotics
Your dentist will prescribe antibiotics if the infection is severe or has spread to other parts of the body to help clear the infection. Also, the dentist will prescribe antibiotics for patients with a weakened immune system. Antibiotics don’t substitute tooth abscess treatment and further treatment will be needed.
Conclusion
You can’t treat tooth abscess at home. So, you have to visit your dentist as soon as possible if you have a toothache or gum swelling to relieve the pain and prevent complications. Tooth abscess treatment depends on the underlying cause. Your dentist may perform a root canal treatment, scaling and root planing, or tooth extraction, depending on the cause of abscess and condition of the tooth. Also, your dentist may prescribe an antibiotic to help clear the infection. Use over-the-counter painkillers to relieve the pain until you can see your dentist.